Efficacy and Safety of Intra-Articular Platelet-Rich Plasma in Osteoarthritis Knee: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34337002
- PMCID: PMC8294028
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/2191926
Efficacy and Safety of Intra-Articular Platelet-Rich Plasma in Osteoarthritis Knee: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) is a common disease in aged adults. Intra-articular (IA) injection of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy is an effective minimally invasive treatment for KOA. We aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) with placebo or other conservative treatments.
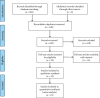
Methods: We conducted a meta-analysis to identify relevant articles from online register databases such as PubMed, Medline, Embase, and the Cochrane Library. The primary outcomes were the visual analogue scale (VAS) score, Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index (WOMAC) score, and International Knee Documentation Committee (IKDC) subjective score. The secondary outcome was the adverse event rate.
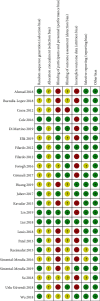
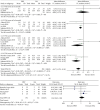
Results: A total of 895 articles were identified, of which 23 randomized controlled trials that met the inclusion criteria were determined as eligible. Compared with placebo, PRP had a lower VAS score and higher IKDC subjective score at the 6th month after treatment and significantly less WOMAC score during the follow-up period. Compared with oral NSAIDs, PRP gained a lower WOMAC score at the 6th month after treatment. The VAS score decreased after treatment when reaching PRP and CS. As compared to the HA, the VAS score, WOMAC score, and IKDC subjective score all revealed better PRP results. There were no significant differences in adverse event rates comparing PRP versus placebo or HA. Different PRP applications did not show significant differences in VAS score in the 1st month and WOMAC score in the 3rd month after treatment.
Conclusion: To compare with the conservative treatments mentioned above, PRP is more effective in relieving symptoms. There were no significant differences between triple PRP application and single PRP application in short-term curative effect.
Copyright © 2021 Mao Hong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest were declared.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hyaluronic Acid Versus Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Prospective, Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Clinical Outcomes and Effects on Intra-articular Biology for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis.Am J Sports Med. 2017 Feb;45(2):339-346. doi: 10.1177/0363546516665809. Epub 2016 Oct 21. Am J Sports Med. 2017. PMID: 28146403 Clinical Trial.
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Hyaluronic Acid for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Am J Sports Med. 2021 Jan;49(1):249-260. doi: 10.1177/0363546520909397. Epub 2020 Apr 17. Am J Sports Med. 2021. PMID: 32302218
-
Platelet-rich plasma versus hyaluronic acid in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2020 Sep 11;15(1):403. doi: 10.1186/s13018-020-01919-9. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 32912243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects and safety of the combination of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and hyaluronic acid (HA) in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020 Apr 11;21(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-03262-w. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020. PMID: 32278352 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-rich plasma versus hyaluronic acid in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Mar;99(11):e19388. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019388. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32176063 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparative Efficacy of Intra-Articular Injection, Physical Therapy, and Combined Treatments on Pain, Function, and Sarcopenia Indices in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 23;24(7):6078. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076078. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047058 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative efficacy of different doses of platelet-rich plasma injection in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Mar 1;20(1):221. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-05650-1. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 40022138 Free PMC article.
-
Pain Management Strategies in Osteoarthritis.Biomedicines. 2024 Apr 4;12(4):805. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12040805. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38672160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Considerations in modern regenerative medicine for osteoarthritis.EFORT Open Rev. 2025 Jun 2;10(6):336-344. doi: 10.1530/EOR-2025-0050. EFORT Open Rev. 2025. PMID: 40459150 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma Power-Mix Gel (ppm)-An Orthobiologic Optimization Protocol Rich in Growth Factors and Fibrin.Gels. 2023 Jul 7;9(7):553. doi: 10.3390/gels9070553. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37504432 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lin K., Yang C. C., Hsu C. J., Yeh M. L., Renn J. H. Intra-articular Injection of Platelet-Rich Plasma Is Superior to Hyaluronic Acid or Saline Solution in the Treatment of Mild to Moderate Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Triple-Parallel, Placebo- Controlled Clinical Trial. Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic & Related Surgery. 2019;35(1):106–117. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2018.06.035. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

