A Genome-Wide Association Study of Age-Related Hearing Impairment in Middle- and Old-Aged Chinese Twins
- PMID: 34337005
- PMCID: PMC8314043
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/3629624
A Genome-Wide Association Study of Age-Related Hearing Impairment in Middle- and Old-Aged Chinese Twins
Abstract
Background: Age-related hearing impairment (ARHI) is considered an unpreventable disorder. We aimed to detect specific genetic variants that are potentially related to ARHI via genome-wide association study (GWAS).
Methods: A sample of 131 dizygotic twins was genotyped for single-nucleotide polymorphism- (SNP-) based GWAS. Gene-based test was performed using VEGAS2. Pathway enrichment analysis was conducted by PASCAL.
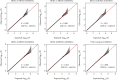
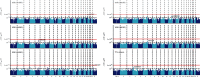
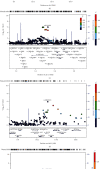
Results: The twins are with a median age of 49 years, of which 128 were females and 134 were males. rs6633657 was the only SNP that reached the genome-wide significance level for better ear hearing level (BEHL) at 2.0 kHz (P = 1.19 × 10-8). Totally, 9, 10, 42, 7, 17, and 5 SNPs were suggestive evidence level for (P < 1 × 10-5) BEHLs at 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 4.0, and 8.0 kHz and pure tone average (PTA), respectively. Several promising genetic regions in chromosomes (near the C20orf196, AQPEP, UBQLN3, OR51B5, OR51I2, OR52D1, GLTP, GIT2, and PARK2) nominally associated with ARHI were identified. Gene-based analysis revealed 165, 173, 77, 178, 170, and 145 genes nominally associated with BEHLs at 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 4.0, and 8.0 kHz and PTA, respectively (P < 0.05). For BEHLs at 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 kHz, the main enriched pathways were phosphatidylinositol signaling system, regulation of ornithine decarboxylase, eukaryotic translation initiation factor (EIF) pathway, amine compound solute carrier (SLC) transporters, synthesis of phosphoinositides (PIPS) at the plasma membrane, and phosphatidylinositols (PI) metabolism.
Conclusions: The genetic variations reported herein are significantly involved in functional genes and regulatory domains that mediate ARHI pathogenesis. These findings provide clues for the further unraveling of the molecular physiology of hearing functions and identifying novel diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets of ARHI.
Copyright © 2021 Haiping Duan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heritability of Age-Related Hearing Loss in Middle-Aged and Elderly Chinese: A Population-Based Twin Study.Ear Hear. 2019 Mar/Apr;40(2):253-259. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000610. Ear Hear. 2019. PMID: 29794565
-
Genome-wide analysis in northern Chinese twins identifies twelve new susceptibility loci for pulmonary function.BMC Genomics. 2024 Dec 30;25(1):1255. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-11165-6. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39736507 Free PMC article.
-
Heritability and genome-wide association analyses of fasting plasma glucose in Chinese adult twins.BMC Genomics. 2020 Jul 18;21(1):491. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-06898-z. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32682390 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental and genetic factors in age-related hearing impairment.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2011 Feb;23(1):3-10. doi: 10.1007/BF03324947. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2011. PMID: 21499014 Review.
-
Progress and prospects in human genetic research into age-related hearing impairment.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:390601. doi: 10.1155/2014/390601. Epub 2014 Jul 22. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25140308 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association between BCL11B gene polymorphisms and age-related hearing loss in the elderly: A case-control study in Qingdao, China.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 3;19(6):e0304770. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304770. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38829888 Free PMC article.
-
Independent and Combined Associations of Sleep Duration, Bedtime, and Polygenic Risk Score with the Risk of Hearing Loss among Middle-Aged and Old Chinese: The Dongfeng-Tongji Cohort Study.Research (Wash D C). 2023 Jun 27;6:0178. doi: 10.34133/research.0178. eCollection 2023. Research (Wash D C). 2023. PMID: 37383219 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu C., Bu X. K., Xing G. Q., et al. Epidemiologic study on hearing impairment and ear diseases in old people. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2006;41(9):661–664. - PubMed
-
- Liu Taoran, Li Xia, Pang Zengchang, Wang Shaojie. Prevalence and influence factors of hearing impairment among rural senior people in Qingdao municipality. Chin Journal of Public Health. 2013;29(8):1147–1150.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

