Hippocampal neurogenesis mediates sex-specific effects of social isolation and exercise on fear extinction in adolescence
- PMID: 34337114
- PMCID: PMC8313755
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2021.100367
Hippocampal neurogenesis mediates sex-specific effects of social isolation and exercise on fear extinction in adolescence
Abstract
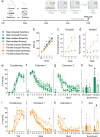
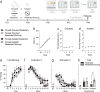
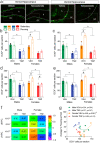
Impaired extinction of conditioned fear is associated with anxiety disorders. Common lifestyle factors, like isolation stress and exercise, may alter the ability to extinguish fear. However, the effect of and interplay between these factors on adolescent fear extinction, and the relevant underlying neural mechanisms are unknown. Here we examined the effects of periadolescent social isolation and physical activity on adolescent fear extinction in rats and explored neurogenesis as a potential mechanism. Isolation stress impaired extinction recall in male adolescents, an effect prevented by exercise. Extinction recall in female adolescents was unaffected by isolation stress. However, exercise disrupted extinction recall in isolated females. Extinction recall in isolated females was positively correlated to the number of immature neurons in the ventral hippocampus, suggesting that exercise affected extinction recall via neurogenesis in females. Pharmacologically suppressing cellular proliferation in isolated adolescents using temozolomide blocked the effect of exercise on extinction recall in both sexes. Together, these findings highlight sex-specific outcomes of isolation stress and exercise on adolescent brain and behavior, and highlights neurogenesis as a potential mechanism underlying lifestyle effects on adolescent fear extinction.
Keywords: Adolescence; Exercise; Neurogenesis; Sex differences; Stress.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Sex-specific effects of CB1 receptor antagonism and stress in adolescence on anxiety, corticosterone concentrations, and contextual fear in adulthood in rats.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2018 Oct;69:119-131. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2018.07.011. Epub 2018 Jul 29. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30063953
-
Deletion of TLX and social isolation impairs exercise-induced neurogenesis in the adolescent hippocampus.Hippocampus. 2018 Jan;28(1):3-11. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22805. Epub 2017 Oct 13. Hippocampus. 2018. PMID: 28972669
-
Adolescent social isolation stress unmasks the combined effects of adolescent exercise and adult inflammation on hippocampal neurogenesis and behavior.Neuroscience. 2017 Dec 4;365:226-236. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.09.020. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Neuroscience. 2017. PMID: 28939260
-
Recalling safety: cooperative functions of the ventromedial prefrontal cortex and the hippocampus in extinction.CNS Spectr. 2007 Mar;12(3):200-6. doi: 10.1017/s1092852900020915. CNS Spectr. 2007. PMID: 17329980 Review.
-
A window of vulnerability: impaired fear extinction in adolescence.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014 Sep;113:90-100. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2013.10.009. Epub 2013 Oct 25. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014. PMID: 24513634 Review.
Cited by
-
Age-specific sex effects in extinction of conditioned fear in rodents.Front Behav Neurosci. 2023 Dec 13;17:1298164. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2023.1298164. eCollection 2023. Front Behav Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38161359 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Sex-dependent effects of chronic exercise on cognitive flexibility but not hippocampal Bdnf in aging mice.Neuronal Signal. 2022 Jan 5;6(1):NS20210053. doi: 10.1042/NS20210053. eCollection 2022 Apr. Neuronal Signal. 2022. PMID: 35036000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The sex-dependent response to psychosocial stress and ischaemic heart disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Apr 21;10:1072042. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1072042. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37153459 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akers K.G., Martinez-Canabal A., Restivo L., Yiu A.P., Cristofaro A.D., Hsiang H.L.L., Wheeler A.L., Guskjolen A., Niibori Y., Shoji H., Ohira K., Richards B.A., Miyakawa T., Josselyn S.A., Frankland P.W. Hippocampal neurogenesis regulates forgetting during adulthood and infancy. Science. 2014;344:598–602. doi: 10.1126/science.1248903. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

