Effects of sevoflurane and adenosine receptor antagonist on the sugammadex-induced recovery from rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade in rodent phrenic nerve-hemidiaphragm tissue specimens
- PMID: 34337892
- PMCID: PMC8326504
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.827
Effects of sevoflurane and adenosine receptor antagonist on the sugammadex-induced recovery from rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade in rodent phrenic nerve-hemidiaphragm tissue specimens
Abstract
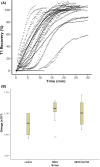
Sevoflurane affects on the A1 receptor in the central nervous system and potentiates the action of neuromuscular blocking agents. In the present study, we investigated whether sevoflurane (SEVO) has the ability to potentiate the neuromuscular blocking effect of rocuronium and if the specific antagonist of adenosine receptor (SLV320) can reverse this effect. In this study, phrenic nerve-hemidiaphragm tissue specimens were obtained from 40 Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats. The specimens were immersed in an organ bath filled with Krebs buffer and stimulated by a train-of-four (TOF) pattern using indirect supramaximal stimulation at 20 s intervals. The specimens were randomly allocated to control, 2-chloroadenosine (CADO), SEVO, or SLV320 + SEVO groups. In the CADO and SLV320 + SEVO groups, CADO and SLV320 were added to the organ bath from the start to a concentration of 10 μM and 10 nM, respectively. We then proceeded with rocuronium-induced blockade of >95% depression of the first twitch tension of TOF (T1) and TOF ratio (TOFR). In the SEVO and SLV320 + SEVO groups, SEVO was added to the Krebs buffer solution to concentration of 400-500 μM for 10 min. Sugammadex-induced T1 and TOFR recovery was monitored for 30 min until >95% of T1 and >0.9 of TOFR were confirmed, and the recovery pattern was compared by plotting these data. T1 recovery in the SEVO and CADO groups was significantly delayed compared with the control and SLV320 + SEVO groups (p < .05). In conclusion, sevoflurane affects on the A1 receptor at the neuromuscular junction and delays sugammadex-induced recovery from neuromuscular blockade.
Keywords: acetylcholine; neuromuscular blockade; neuromuscular blocking agent; rocuronium; sevoflurane; sugammadex.
© 2021 The Authors. Pharmacology Research & Perspectives published by British Pharmacological Society and American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare in association with this work.
Figures


References
-
- Tas PW, Eisemann C, Roewer N. Indirect activation of adenosine A1 receptors in cultured rat hippocampal neurons by volatile anaesthetics. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2005;22:694‐702. - PubMed
-
- Haulilca I, Ababei L, Branisteanu D, Topoliceanu F. Preliminary data on the possible hypnogenic role of adenosine. J Neurochem. 1973;21:1019‐1020. - PubMed
-
- Segerdahl M, Ekblom A, Sandelin K, Wickman M, Sollevi A. Peroperative adenosine infusion reduces the requirements for isoflurane and postoperative analgesics. Anesth Analg. 1995;80:1145‐1149. - PubMed
-
- Turan A, Kasuya Y, Govinda R, et al. The effect of aminophylline on loss of consciousness, bispectral index, propofol requirement, and minimum alveolar concentration of desflurane in volunteers. Anesth Analg. 2010;110:449‐454. - PubMed
-
- Turan A, Memiş D, Karamanlioğlu B, Çolak A, Pamukçu Z, Turan N. Effect of aminophylline on recovery from sevoflurane anaesthesia. Eur J Anaesth. 2002;19:452‐454. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

