Histone deacetylase 9 promotes endothelial-mesenchymal transition and an unfavorable atherosclerotic plaque phenotype
- PMID: 34338228
- PMCID: PMC8321575
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI131178
Histone deacetylase 9 promotes endothelial-mesenchymal transition and an unfavorable atherosclerotic plaque phenotype
Abstract
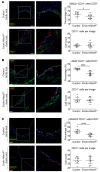
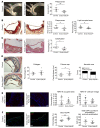
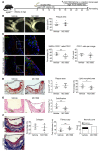
Endothelial-mesenchymal transition (EndMT) is associated with various cardiovascular diseases and in particular with atherosclerosis and plaque instability. However, the molecular pathways that govern EndMT are poorly defined. Specifically, the role of epigenetic factors and histone deacetylases (HDACs) in controlling EndMT and the atherosclerotic plaque phenotype remains unclear. Here, we identified histone deacetylation, specifically that mediated by HDAC9 (a class IIa HDAC), as playing an important role in both EndMT and atherosclerosis. Using in vitro models, we found class IIa HDAC inhibition sustained the expression of endothelial proteins and mitigated the increase in mesenchymal proteins, effectively blocking EndMT. Similarly, ex vivo genetic knockout of Hdac9 in endothelial cells prevented EndMT and preserved a more endothelial-like phenotype. In vivo, atherosclerosis-prone mice with endothelial-specific Hdac9 knockout showed reduced EndMT and significantly reduced plaque area. Furthermore, these mice displayed a more favorable plaque phenotype, with reduced plaque lipid content and increased fibrous cap thickness. Together, these findings indicate that HDAC9 contributes to vascular pathology by promoting EndMT. Our study provides evidence for a pathological link among EndMT, HDAC9, and atherosclerosis and suggests that targeting of HDAC9 may be beneficial for plaque stabilization or slowing the progression of atherosclerotic disease.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Cardiology; Endothelial cells; Epigenetics; Vascular Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL126949/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL125863/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CH/11/2/28733/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 HL142097/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007824/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL134354/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL135093/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL130423/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG064895/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA154683/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/14/3/30706/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 HL148167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR070029/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

