SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: pathogenesis, vaccines, and potential therapies
- PMID: 34339040
- PMCID: PMC8326314
- DOI: 10.1007/s15010-021-01677-8
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: pathogenesis, vaccines, and potential therapies
Abstract
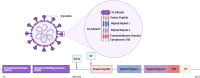
Purpose: COVID-19 pandemic has emerged as a result of infection by the deadly pathogenic severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), causing enormous threats to humans. Coronaviruses are distinguished by a clove-like spike (S) protein, which plays a key role in viral pathogenesis, evolutions, and transmission. The objectives of this study are to investigate the distinctive structural features of SARS-CoV-2 S protein, its essential role in pathogenesis, and its use in the development of potential therapies and vaccines.
Methodology: A literature review was conducted to summarize, analyze, and interpret the available scientific data related to SARS-CoV-2 S protein in terms of characteristics, vaccines development and potential therapies.
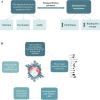
Results: The data indicate that S protein subunits and their variable conformational states significantly affect the virus pathogenesis, infectivity, and evolutionary mutation. A considerable number of potential natural and synthetic therapies were proposed based on S protein. Additionally, neutralizing antibodies were recently approved for emergency use. Furthermore, several vaccines utilizing the S protein were developed.
Conclusion: A better understanding of S protein features, structure and mutations facilitate the recognition of the importance of SARS-CoV-2 S protein in viral infection, as well as the development of therapies and vaccines. The efficacy and safety of these therapeutic compounds and vaccines are still controversial. However, they may potentially reduce or prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection, leading to a significant reduction of the global health burden of this pandemic.
Keywords: Mutations; Pathogenesis; SARS-CoV-2; Spike protein; Treatments; Vaccines.
© 2021. Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine. (2021).
-
- U.S. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS.gov). Monoclonal antibody COVID-19 infusion. (2021).
-
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: FDA revokes emergency use authorization for monoclonal antibody bamlanivimab. (2021).
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). AZD1222 vaccine against COVID-19 developed by Oxford University and Astra Zeneca: Background paper (2021)
-
- Johnson & Johnson. Positive new data for Johnson & Johnson single-shot COVID-19 vaccine on activity against delta variant and long-lasting durability of response. (2021) July 1, 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

