Neurocomputational models of altruistic decision-making and social motives: Advances, pitfalls, and future directions
- PMID: 34340256
- PMCID: PMC9286344
- DOI: 10.1002/wcs.1571
Neurocomputational models of altruistic decision-making and social motives: Advances, pitfalls, and future directions
Abstract
This article discusses insights from computational models and social neuroscience into motivations, precursors, and mechanisms of altruistic decision-making and other-regard. We introduce theoretical and methodological tools for researchers who wish to adopt a multilevel, computational approach to study behaviors that promote others' welfare. Using examples from recent studies, we outline multiple mental and neural processes relevant to altruism. To this end, we integrate evidence from neuroimaging, psychology, economics, and formalized mathematical models. We introduce basic mechanisms-pertinent to a broad range of value-based decisions-and social emotions and cognitions commonly recruited when our decisions involve other people. Regarding the latter, we discuss how decomposing distinct facets of social processes can advance altruistic models and the development of novel, targeted interventions. We propose that an accelerated synthesis of computational approaches and social neuroscience represents a critical step towards a more comprehensive understanding of altruistic decision-making. We discuss the utility of this approach to study lifespan differences in social preference in late adulthood, a crucial future direction in aging global populations. Finally, we review potential pitfalls and recommendations for researchers interested in applying a computational approach to their research. This article is categorized under: Economics > Interactive Decision-Making Psychology > Emotion and Motivation Neuroscience > Cognition Economics > Individual Decision-Making.
Keywords: decision neuroscience; drift diffusion models; prosociality; social affect and cognition (theory of mind); social choice tasks.
© 2021 The Authors. WIREs Cognitive Science published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures
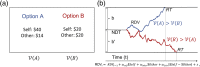
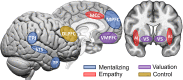
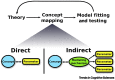
References
-
- Akaike, H. (1974). A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 19(6), 716–723.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

