LrpCBA pilus proteins of gut-dwelling Ligilactobacillus ruminis: crystallization and X-ray diffraction analysis
- PMID: 34341189
- PMCID: PMC8329715
- DOI: 10.1107/S2053230X21007263
LrpCBA pilus proteins of gut-dwelling Ligilactobacillus ruminis: crystallization and X-ray diffraction analysis
Abstract
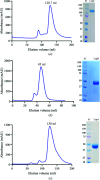
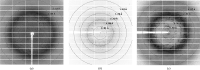
Adhesion to host surfaces for bacterial survival and colonization involves a variety of molecular mechanisms. Ligilactobacillus ruminis, a strict anaerobe and gut autochthonous (indigenous) commensal, relies on sortase-dependent pili (LrpCBA) for adherence to the intestinal inner walls, thereby withstanding luminal content flow. Here, the LrpCBA pilus is a promiscuous binder to gut collagen, fibronectin and epithelial cells. Structurally, the LrpCBA pilus displays a representative hetero-oligomeric arrangement and consists of three types of pilin subunit, each with its own location and function, i.e. tip LrpC for adhesion, basal LrpB for anchoring and backbone LrpA for length. To provide further structural insights into the assembly, anchoring and functional mechanisms of sortase-dependent pili, each of the L. ruminis pilus proteins was produced recombinantly for crystallization and X-ray diffraction analysis. Crystals of LrpC, LrpB, LrpA and truncated LrpA generated by limited proteolysis were obtained and diffracted to resolutions of 3.0, 1.5, 2.2 and 1.4 Å, respectively. Anomalous data were also collected from crystals of selenomethionine-substituted LrpC and an iodide derivative of truncated LrpA. Successful strategies for protein production, crystallization and derivatization are reported.
Keywords: Ligilactobacillus ruminis; LrpCBA pilus; autochthonous commensals; backbone LrpA; basal LrpB; gut bacteria; intestine; pilins; tip LrpC.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human Gut-Commensalic Lactobacillus ruminis ATCC 25644 Displays Sortase-Assembled Surface Piliation: Phenotypic Characterization of Its Fimbrial Operon through In Silico Predictive Analysis and Recombinant Expression in Lactococcus lactis.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 28;10(12):e0145718. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145718. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26709916 Free PMC article.
-
The crystal structure of the N-terminal domain of the backbone pilin LrpA reveals a new closure-and-twist motion for assembling dynamic pili in Ligilactobacillus ruminis.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2024 Jul 1;80(Pt 7):474-492. doi: 10.1107/S2059798324005114. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2024. PMID: 38935340
-
Crystallization and X-ray diffraction analysis of SpaE, a basal pilus protein from the gut-adapted Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2017 Jun 1;73(Pt 6):321-327. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X17006963. Epub 2017 May 25. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2017. PMID: 28580919 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Molecular Insights about Lactobacillar Sortase-Dependent Piliation.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jul 18;18(7):1551. doi: 10.3390/ijms18071551. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28718795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pilus biogenesis of Gram-positive bacteria: Roles of sortases and implications for assembly.Protein Sci. 2017 Aug;26(8):1458-1473. doi: 10.1002/pro.3191. Epub 2017 May 15. Protein Sci. 2017. PMID: 28493331 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Review of the Mechanisms of Bacterial Colonization of the Mammal Gut.Microorganisms. 2024 May 19;12(5):1026. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12051026. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38792855 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Danne, C. & Dramsi, S. (2012). Res. Microbiol. 163, 645–658. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

