Current issues of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease surgical treatment in children
- PMID: 34341194
- PMCID: PMC8362913
- DOI: 10.4103/ajps.AJPS_104_20
Current issues of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease surgical treatment in children
Abstract
Gastro-oesophageal reflux (GER) disease is one of the most common diseases amongst a wide range of chronic inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in children of all ages, significantly impairing the quality of life of the child and posing a serious threat to the health of the patient. From 2008 to 2019, 134 patients aging from 6 months to 12 years were hospitalised at the Scientific Center for Pediatrics and Pediatric Surgery including 69 (51%) infants. Of them, 51 (38%) were the patients with persistent manifestations of regurgitation, despite an outpatient course of conservative therapy; 29 (22%) patients with recurrent reflux-associated pneumonia; also, 35 (26%) children with GER in the structure of the main pathology of the central nervous system, as well as 19 (14%) patients after surgery of the anastomosis of the oesophagus with its atresia. One hundred and seven (79.8%) patients underwent surgery. Nissen oesophagofundoplication was traditionally performed in 41 (38%) patients, in combination with Stamm gastrostomy in 14 (34%), with Mikulich pyloroplasty in 9 (22%) and in combination with gastrostomy and pyloroplasty in 12 (29%) children. Laparoscopic Nissen oesophagofundoplication was used in 16 (15%) cases. Thall oesophagofundoplication was performed in 48 (45%) patients, while in two (2%) cases, Boerema gastropexy was conducted. The immediate results were studied in all 107 patients. Complications in the form of gastric distress syndrome were revealed in four (3.7%) patients who did not undergo pyloroplasty, which in two (1.9%) cases required additional surgery of the stomach draining, whereas in the other two (1.9%) patients, the distress syndrome was stopped conservatively. A dumping syndrome was identified in two (1.9%) patients. Timely recognition of the pathological process, its nature and prevalence determines the indications for the use of various methods of operation, which are based on an individual approach to each patient.
Keywords: Children; gastro-oesophageal reflux; oesophagitis; oesophagofundoplication.
Conflict of interest statement
None
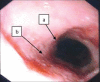
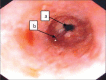
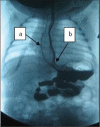
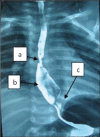
Figures
Similar articles
-
Current issues of GERD surgical treatment in children.Afr J Paediatr Surg. 2021 Jan-Mar;18(1):47-52. doi: 10.4103/ajps.AJPS_61_19. Afr J Paediatr Surg. 2021. PMID: 33595542 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of alkaline reflux in children after Nissen fundoplication and pyloroplasty.J Am Coll Surg. 1994 Jan;178(1):1-5. J Am Coll Surg. 1994. PMID: 8156109
-
A comparison of Nissen fundoplication and Boerema gastropexy in the surgical treatment of gastro-oesophageal reflux in children.Br J Surg. 1983 Feb;70(2):125-7. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800700224. Br J Surg. 1983. PMID: 6824899
-
Gastroesophageal reflux in childhood.Curr Probl Surg. 1996 Jan;33(1):1-70. Curr Probl Surg. 1996. PMID: 8536488 Review.
-
Fundoplication in children with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease.J Paediatr Child Health. 2002 Apr;38(2):156-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1754.2002.00756.x. J Paediatr Child Health. 2002. PMID: 12030997 Review.
References
-
- Altorki NK, Skinner DB, Segalin A, Stephens JK, Ferguson MK, Little AG. Indications for esophagectomy in nonmalignant Barrett's esophagus: A 10-year experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990;49:724–6. - PubMed
-
- Hassall E. Decisions in diagnosing and managing chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease in children. J Pediatr. 2005;146:S3–12. - PubMed
-
- Guimaraes E, Marguet C, Camargos P. Treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Pediatr. 2006;82:133–45. - PubMed
-
- Lasser MS, Liao JG, Burd RS. National trends in the use of antireflux procedures for children. Pediatrics. 2006;118:1828–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
