Emerging liver organoid platforms and technologies
- PMID: 34341842
- PMCID: PMC8329140
- DOI: 10.1186/s13619-021-00089-1
Emerging liver organoid platforms and technologies
Abstract
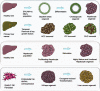
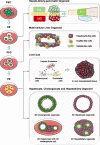
Building human organs in a dish has been a long term goal of researchers in pursue of physiologically relevant models of human disease and for replacement of worn out and diseased organs. The liver has been an organ of interest for its central role in regulating body homeostasis as well as drug metabolism. An accurate liver replica should contain the multiple cell types found in the organ and these cells should be spatially organized to resemble tissue structures. More importantly, the in vitro model should recapitulate cellular and tissue level functions. Progress in cell culture techniques and bioengineering approaches have greatly accelerated the development of advance 3-dimensional (3D) cellular models commonly referred to as liver organoids. These 3D models described range from single to multiple cell type containing cultures with diverse applications from establishing patient-specific liver cells to modeling of chronic liver diseases and regenerative therapy. Each organoid platform is advantageous for specific applications and presents its own limitations. This review aims to provide a comprehensive summary of major liver organoid platforms and technologies developed for diverse applications.
Keywords: Disease models; Liver; Organoids; Regenerative therapy; Stem cells.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Achberger K, Probst C, Haderspeck J, Bolz S, Rogal J, Chuchuy J, Nikolova M, Cora V, Antkowiak L, Haq W, Shen N, Schenke-Layland K, Ueffing M, Liebau S, Loskill P. Merging organoid and organ-on-a-chip technology to generate complex multi-layer tissue models in a human retina-on-a-chip platform. eLife. 2019;8:e46188. doi: 10.7554/eLife.46188. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akbari S, Sevinç GG, Ersoy N, Basak O, Kaplan K, Sevinç K, Ozel E, Sengun B, Enustun E, Ozcimen B, Bagriyanik A, Arslan N, Önder TT, Erdal E. Robust, Long-term culture of endoderm-derived hepatic organoids for disease modeling. Stem Cell Rep. 2019;13(4):627–641. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2019.08.007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Almeda-Valdés P, Aguilar-Olivos NE, Uribe M, Méndez-Sánchez N. Chapter 25 - the metabolic syndrome, oxidative stress, and the liver. In: Muriel P, editor. Liver pathophysiology. Boston: Academic; 2017. pp. 323–329.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
