Easy and reliable maximum a posteriori Bayesian estimation of pharmacokinetic parameters with the open-source R package mapbayr
- PMID: 34342170
- PMCID: PMC8520754
- DOI: 10.1002/psp4.12689
Easy and reliable maximum a posteriori Bayesian estimation of pharmacokinetic parameters with the open-source R package mapbayr
Abstract
Pharmacokinetic (PK) parameter estimation is a critical and complex step in the model-informed precision dosing (MIPD) approach. The mapbayr package was developed to perform maximum a posteriori Bayesian estimation (MAP-BE) in R from any population PK model coded in mrgsolve. The performances of mapbayr were assessed using two approaches. First, "test" models with different features were coded, for example, first-order and zero-order absorption, lag time, time-varying covariates, Michaelis-Menten elimination, combined and exponential residual error, parent drug and metabolite, and small or large inter-individual variability (IIV). A total of 4000 PK profiles (combining single/multiple dosing and rich/sparse sampling) were simulated from each test model, and MAP-BE of parameters was performed in both mapbayr and NONMEM. Second, a similar procedure was conducted with seven "real" previously published models to compare mapbayr and NONMEM on a PK outcome used in MIPD. For the test models, 98% of mapbayr estimations were identical to those given by NONMEM. Some discordances could be observed when dose-related parameters were estimated or when models with large IIV were used. The exploration of objective function values suggested that mapbayr might outdo NONMEM in specific cases. For the real models, a concordance close to 100% on PK outcomes was observed. The mapbayr package provides a reliable solution to perform MAP-BE of PK parameters in R. It also includes functions dedicated to data formatting and reporting and enables the creation of standalone Shiny web applications dedicated to MIPD, whatever the model or the clinical protocol and without additional software other than R.
© 2021 The Authors. CPT: Pharmacometrics & Systems Pharmacology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no competing interests for this work.
Figures
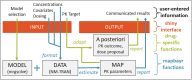

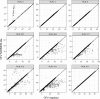

References
-
- Definitions of TDM &CT. https://www.iatdmct.org/about‐us/about‐association/about‐definitions‐tdm.... Accessed June 21, 2021.
-
- Ting LSL, Villeneuve E, Ensom MHH. Beyond cyclosporine: A systematic review of limited sampling strategies for other immunosuppressants. Ther Drug Monit. 2006;28:419‐430. - PubMed
-
- Chatelut E, Pivot X, Otto J, et al. A limited sampling strategy for determining carboplatin AUC and monitoring drug dosage. Eur J Cancer. 2000;36:264‐269. - PubMed
-
- Tranchand B, Amsellem C, Chatelut E, et al. A limited‐sampling strategy for estimation of etoposide pharmacokinetics in cancer patients. Cancer Chemotherapy Pharmacology. 1999;43:316‐322. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

