Within-host evolutionary dynamics of seasonal and pandemic human influenza A viruses in young children
- PMID: 34342576
- PMCID: PMC8382297
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.68917
Within-host evolutionary dynamics of seasonal and pandemic human influenza A viruses in young children
Abstract
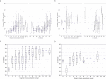
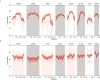
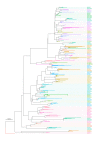
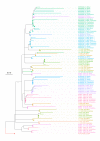
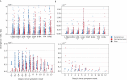
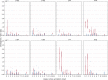
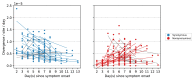
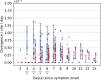
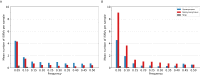
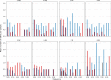
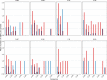
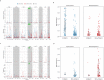
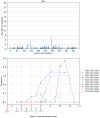
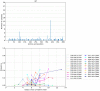
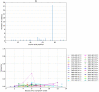
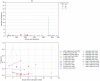
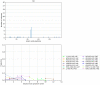
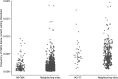
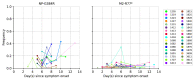
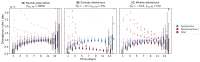
The evolution of influenza viruses is fundamentally shaped by within-host processes. However, the within-host evolutionary dynamics of influenza viruses remain incompletely understood, in part because most studies have focused on infections in healthy adults based on single timepoint data. Here, we analyzed the within-host evolution of 82 longitudinally sampled individuals, mostly young children, infected with A/H1N1pdm09 or A/H3N2 viruses between 2007 and 2009. For A/H1N1pdm09 infections during the 2009 pandemic, nonsynonymous minority variants were more prevalent than synonymous ones. For A/H3N2 viruses in young children, early infection was dominated by purifying selection. As these infections progressed, nonsynonymous variants typically increased in frequency even when within-host virus titers decreased. Unlike the short-lived infections of adults where de novo within-host variants are rare, longer infections in young children allow for the maintenance of virus diversity via mutation-selection balance creating potentially important opportunities for within-host virus evolution.
Keywords: evolutionary biology; evolutionary dynamics; human; infectious disease; influenza virus; microbiology; mutation-selection balance; virus.
© 2021, Han et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AH, ZF, MW, RV, NT, TL, TP, DD, TT, MH, TN, QL, TL, TH, KC, PP, VN, MN, VN, TD, TT, HW, PH, AF, Hv, DE, Md, CR No competing interests declared
Figures






References
-
- Berkhoff EG, Boon AC, Nieuwkoop NJ, Fouchier RA, Sintnicolaas K, Osterhaus AD, Rimmelzwaan GF. A mutation in the HLA-B*2705-restricted NP383-391 epitope affects the human influenza A virus-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response in vitro. Journal of Virology. 2004;78:5216–5222. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.10.5216-5222.2004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berkhoff EG, de Wit E, Geelhoed-Mieras MM, Boon AC, Symons J, Fouchier RA, Osterhaus AD, Rimmelzwaan GF. Functional constraints of influenza A virus epitopes limit escape from cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Journal of Virology. 2005;79:11239–11246. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.17.11239-11246.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

