Selective dephosphorylation by PP2A-B55 directs the meiosis I-meiosis II transition in oocytes
- PMID: 34342579
- PMCID: PMC8370769
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.70588
Selective dephosphorylation by PP2A-B55 directs the meiosis I-meiosis II transition in oocytes
Abstract
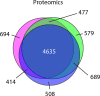
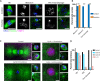
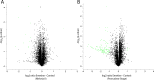
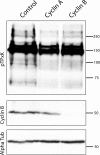
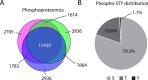
Meiosis is a specialized cell cycle that requires sequential changes to the cell division machinery to facilitate changing functions. To define the mechanisms that enable the oocyte-to-embryo transition, we performed time-course proteomics in synchronized sea star oocytes from prophase I through the first embryonic cleavage. Although we found that protein levels were broadly stable, our analysis reveals that dynamic waves of phosphorylation underlie each meiotic stage. We found that the phosphatase PP2A-B55 is reactivated at the meiosis I/meiosis II (MI/MII) transition, resulting in the preferential dephosphorylation of threonine residues. Selective dephosphorylation is critical for directing the MI/MII transition as altering PP2A-B55 substrate preferences disrupts key cell cycle events after MI. In addition, threonine to serine substitution of a conserved phosphorylation site in the substrate INCENP prevents its relocalization at anaphase I. Thus, through its inherent phospho-threonine preference, PP2A-B55 imposes specific phosphoregulated behaviors that distinguish the two meiotic divisions.
Keywords: cell biology; meiosis; patiria miniata; phosphatases; proteomics.
© 2021, Swartz et al.
Conflict of interest statement
SS, HN, BM, MA, IC, AK No competing interests declared
Figures









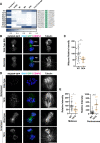

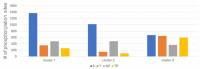
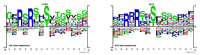
References
-
- Adhikari D, Diril MK, Busayavalasa K, Risal S, Nakagawa S, Lindkvist R, Shen Y, Coppola V, Tessarollo L, Kudo NR, Kaldis P, Liu K. Mastl is required for timely activation of APC/C in meiosis I and Cdk1 reactivation in meiosis II. Journal of Cell Biology. 2014;206:843–853. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201406033. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bachmann M, Kosan C, Xing PX, Montenarh M, Hoffmann I, Möröy T. The oncogenic serine/threonine kinase Pim-1 directly phosphorylates and activates the G2/M specific phosphatase Cdc25C. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology. 2006;38:430–443. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2005.10.010. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

