The role of mouthwash sampling in SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis
- PMID: 34342767
- PMCID: PMC8328810
- DOI: 10.1007/s10096-021-04320-4
The role of mouthwash sampling in SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis
Abstract
Background: The current practice of COVID-19 diagnosis worldwide is the use of oro-nasopharyngeal (ONP) swabs. Our study aim was to explore mouthwash (MW) as an alternative diagnostic method, in light of the disadvantages of ONP swabs.
Methods: COVID-19 outpatients molecular-confirmed by ONP swab were repeatedly examined with ONP swab and MW with normal saline (0.9%). Other types of fluids were compared to normal saline. The Cq values obtained with each method were compared.
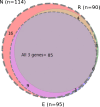
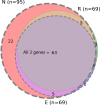
Results: Among 137 pairs of ONP swabs and MW samples, 84.6% (116/137) of ONP swabs were positive by at least one of the genes (N, E, R). However MW detected 70.8% (97/137) of samples as positive, which means 83.6% (97/116) out of positive ONP swabs, missing mainly Cq value > 30. In both methods, the N gene was the most sensitive one. Therefore, MW samples targeting N gene, which was positive in 95/137 (69.3%), are comparable to ONP swabs targeting E and R genes which gave equal results-95/137 (69.3%) and 90/137 (65.7%), respectively. Comparing saline MW to distilled water gave equal results, while commercial mouth-rinsing solutions were less sensitive.
Conclusions: MW with normal saline, especially when tested by N gene, can effectively detect COVID-19 patients. Furthermore, this method was not inferior when compared to R and E genes of ONP swabs, which are common targets in many laboratories around the world.
Keywords: COVID-19; Gargling; Mouth rinse; Saliva; Throat-wash.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization (2020) Weekly Operational Update on COVID-19, 4 September 2020. World Health Organization 1:6
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

