SNP-based assessment of genetic purity and diversity in maize hybrid breeding
- PMID: 34343170
- PMCID: PMC8330893
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249505
SNP-based assessment of genetic purity and diversity in maize hybrid breeding
Abstract
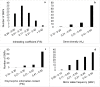
Assessment of genetic purity of parental inbred lines and their resultant F1 hybrids is an essential quality control check in maize hybrid breeding, variety release and seed production. In this study, genetic purity, parent-offspring relationship and diversity among the inbred lines were assessed using 92 single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers. A total of 188 maize genotypes, comprising of 26 inbred lines, four doubled haploid (DH) lines and 158 single-cross maize hybrids were investigated in this study using Kompetitive Allele Specific Polymerase Chain Reaction (KASP) genotyping assays. The bi-allelic data was analyzed for genetic purity and diversity parameters using GenAlex software. The SNP markers were highly polymorphic and 90% had polymorphic information content (PIC) values of > 0.3. Pairwise genetic distances among the lines ranged from 0.05 to 0.56, indicating a high level of dissimilarity among the inbred lines. A maximum genetic distance of (0.56) was observed between inbred lines CKDHL0089 and CML443 while the lowest (0.05) was between I-42 and I-40. The majority (67%) of the inbred lines studied were genetically pure with residual heterozygosity of <5%, while only 33% had heterozygosity levels of >5%. Inbred lines, which were not pure, require purification through further inbreeding. Cluster analysis partitioned the lines into three distinct genetic clusters with the potential to contribute new beneficial alleles to the maize breeding program. Out of the 68 hybrids (43%) that passed the parent-offspring test, seven hybrids namely; SCHP29, SCHP95, SCHP94, SCHP134, SCHP44, SCHP114 and SCHP126, were selected as potential candidates for further evaluation and release due to their outstanding yield performance.
Conflict of interest statement
No authors have competing interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Development of genic KASP SNP markers from RNA-Seq data for map-based cloning and marker-assisted selection in maize.BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Mar 26;21(1):157. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-02932-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 33771110 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic diversity and population structure of early and extra-early maturing maize germplasm adapted to sub-Saharan Africa.BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Feb 17;21(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-02829-6. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 33596835 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic diversity and population structure analyses of tropical maize inbred lines using Single Nucleotide Polymorphism markers.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 24;20(1):e0315463. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0315463. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39854488 Free PMC article.
-
Maize In Planta Haploid Inducer Lines: A Cornerstone for Doubled Haploid Technology.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2288:25-48. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1335-1_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34270003 Review.
-
Doubled Haploid Technology: Opportunities and Challenges for the Rapid Generation of Maize Homozygous Lines.Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2025 Mar 3;2025(3):pdb.top108437. doi: 10.1101/pdb.top108437. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2025. PMID: 39414387 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Seed Origin and Genetic Drift of Improved Rice Variety IR841 in Benin.Rice (N Y). 2023 Oct 25;16(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12284-023-00657-w. Rice (N Y). 2023. PMID: 37878087 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Fingerprinting and Hybridity Authentication in Cowpea Using Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Based Kompetitive Allele-Specific PCR Assay.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Oct 5;12:734117. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.734117. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34675950 Free PMC article.
-
Development of KASP markers, SNP fingerprinting and population genetic analysis of Cymbidium ensifolium (L.) Sw. germplasm resources in China.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jan 8;15:1460603. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1460603. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 39845486 Free PMC article.
-
DArTseq-based SNP markers reveal high genetic diversity among early generation fall armyworm tolerant maize inbred lines.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 17;19(4):e0294863. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294863. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38630672 Free PMC article.
-
Efficiency of Biological Typing Methods in Maize Hybrid Genetic Purity Estimation.Genes (Basel). 2023 May 30;14(6):1195. doi: 10.3390/genes14061195. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372375 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shiferaw B, Prasanna BM, Hellin J, Bänziger M. Crops that feed the world 6. Past successes and future challenges to the role played by maize in global food security. Food Security. 2011; 3:307–327.
-
- Gowda M, Worku M, Nair SK, Palacios-Rojas N, Huestis G, Prasanna B. Quality Assurance/Quality Control (QA/QC) in Maize Breeding and Seed Production: Theory and Practice. CIMMYT. 2017.
-
- Semagn K, Bjørnstad A, Ndjiondjop M. An overview of molecular marker methods for plants. African Journal of Biotechnology. 2006; 5:2540–2568.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

