Reduction in hospitalised COPD exacerbations during COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 34343205
- PMCID: PMC8330941
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0255659
Reduction in hospitalised COPD exacerbations during COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Reports have suggested a reduction in exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, particularly hospital admissions for severe exacerbations. However, the magnitude of this reduction varies between studies.
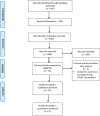
Method: Electronic databases were searched from January 2020 to May 2021. Two independent reviewers screened titles and abstracts and, when necessary, full text to determine if studies met inclusion criteria. A modified version of the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale was used to assess study quality. A narrative summary of eligible studies was synthesised, and meta-analysis was conducted using a random effect model to pool the rate ratio and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) for hospital admissions. Exacerbation reduction was compared against the COVID-19 Containment and Health Index.
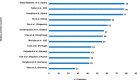
Results: A total of 13 of 745 studies met the inclusion criteria and were included in this review, with data from nine countries. Nine studies could be included in the meta-analysis. The pooled rate ratio of hospital admissions for COPD exacerbations during the pandemic period was 0.50 (95% CI 0.44-0.57). Findings on the rate of community-treated exacerbations were inconclusive. Three studies reported a significant decrease in the incidence of respiratory viral infections compared with the pre-pandemic period. There was not a significant relationship between exacerbation reduction and the COVID-19 Containment and Health Index (rho = 0.20, p = 0.53).
Conclusion: There was a 50% reduction in admissions for COPD exacerbations during the COVID-19 pandemic period compared to pre-pandemic times, likely associated with a reduction in respiratory viral infections that trigger exacerbations. Future guidelines should consider including recommendations on respiratory virus infection control measures to reduce the burden of COPD exacerbations beyond the pandemic period.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- WHO. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/chronic-obstructive-pul...
-
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. 2021 [cited 2021 01/03/2021]. Available from: https://goldcopd.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/GOLD-2020-POCKET-GUIDE-F....
-
- Alqahtani JS, Oyelade T, Aldhahir AM, Alghamdi SM, Almehmadi M, Alqahtani AS, et al. Prevalence, Severity and Mortality associated with COPD and Smoking in patients with COVID-19: A Rapid Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PloS one. 2020;15(5):e0233147–e. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233147 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

