Executive summary of the 2020 clinical practice guidelines for the management of hypertension in the Philippines
- PMID: 34343391
- PMCID: PMC8678709
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.14335
Executive summary of the 2020 clinical practice guidelines for the management of hypertension in the Philippines
Abstract
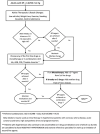
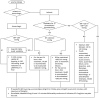
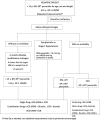
Hypertension is the most common cause of death and disability worldwide with its prevalence rising in low to middle income countries. It remains to be an important cause of morbidity and mortality in the Philippines with poor BP control as one of the main causes. Different societies and groups worked and collaborated together to develop the 2020 Philippine Clinical Practice Guidelines of hypertension arising for the need to come up with a comprehensive local practice guideline for the diagnosis, treatment, and follow up of persons with hypertension. A technical working group was organized into six clusters that analyzed the 30 clinical questions commonly asked in practice, looking into the definition of hypertension, treatment thresholds, blood pressure targets, and appropriate medications to reach targets. This guideline also includes recommendations for the specific management of hypertension among individuals with uncomplicated hypertension, hypertension among those with diabetes, stroke, chronic kidney disease, as well as hypertension among pregnant women and pediatric populations. It also looked into the appropriate screening and monitoring of patients when managing hypertension, and identification of groups who are at high risk for cardiovascular (CV) events. The ADAPTE process was used in developing the statements and recommendations which were then presented to a panel of experts for discussion and approval to come up with the final statements. This guideline aims to aid Filipino healthcare professionals to provide evidence-based care for persons with hypertension and help those with hypertension adequately control their blood pressure and reduce their CV risk.
Keywords: hypertension-general; lifestyle modification/hypertension; treatment and diagnosis/guidelines.
© 2021 The Authors. The Journal of Clinical Hypertension published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures
References
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. 2005;365(9455):217‐223. - PubMed
-
- GBD 2013 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks in 188 countries, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;386(10010):2287‐2323. - PMC - PubMed
-
- http://enutrition.fnri.dost.gov.ph/site/uploads/Adults_and_Elderly.pdf. Accessed: 27 November, 2020
-
- https://g‐i‐n.net/document‐store/working‐groups‐documents/adaptation/res... Accessed: 08 February, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical