Protein kinase R and the integrated stress response drive immunopathology caused by mutations in the RNA deaminase ADAR1
- PMID: 34343497
- PMCID: PMC8446335
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.07.001
Protein kinase R and the integrated stress response drive immunopathology caused by mutations in the RNA deaminase ADAR1
Abstract
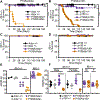
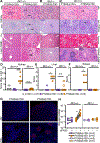
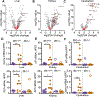
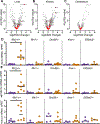
The RNA deaminase ADAR1 is an essential negative regulator of the RNA sensor MDA5, and loss of ADAR1 function triggers inappropriate activation of MDA5 by self-RNAs. Mutations in ADAR, the gene that encodes ADAR1, cause human immune diseases, including Aicardi-Goutières syndrome (AGS). However, the mechanisms of MDA5-dependent disease pathogenesis in vivo remain unknown. Here we generated mice with a single amino acid change in ADAR1 that models the most common human ADAR AGS mutation. These Adar mutant mice developed lethal disease that required MDA5, the RIG-I-like receptor LGP2, type I interferons, and the eIF2α kinase PKR. A small-molecule inhibitor of the integrated stress response (ISR) that acts downstream of eIF2α phosphorylation prevented immunopathology and rescued the mice from mortality. These findings place PKR and the ISR as central components of immunopathology in vivo and identify therapeutic targets for treatment of human diseases associated with the ADAR1-MDA5 axis.
Keywords: ADAR1; Aicardi-Goutières syndrome; LGP2; MDA5; PKR; integrated stress response; interferons.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests C.S. is an employee of Calico Life Sciences and is listed as an inventor on a patent application WO2017193063 describing 2BAct. D.B.S. is a co-founder and shareholder of Danger Bio, LLC, and a scientific advisor for Related Sciences, LLC.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

