Endophenotypical drift in Huntington's disease: a 5-year follow-up study
- PMID: 34344392
- PMCID: PMC8336065
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-021-01967-2
Endophenotypical drift in Huntington's disease: a 5-year follow-up study
Abstract
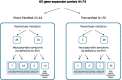
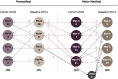
Background: Huntington's disease (HD) is clinically characterized by progressing motor, cognitive and psychiatric symptoms presenting as varying phenotypes within these three major symptom domains. The disease is caused by an expanded CAG repeat tract in the huntingtin gene and the pathomechanism leading to these endophenotypes is assumed to be neurodegenerative. In 2012/2013 we recruited 107 HD gene expansion carriers (HDGECs) and examined the frequency of the three cardinal symptoms and in 2017/2018 we followed up 74 HDGECs from the same cohort to describe the symptom trajectories and individual drift between the endophenotypes as well as potential predictors of progression and remission.
Results: We found higher age to reduce the probability of improving on psychiatric symptoms; increasing disease burden score ((CAG-35.5) * age) to increase the risk of developing cognitive impairment; increasing disease burden score and shorter education to increase the risk of motor onset while lower disease burden score and higher Mini Mental State Examination increased the probability of remaining asymptomatic. We found 23.5% (N = 8) to improve from their psychiatric symptoms.
Conclusions: There is no clear pattern in the development of or drift between endophenotypes. In contrast to motor and cognitive symptoms we find that psychiatric symptoms may resolve and thereby not entirely be caused by neurodegeneration. The probability of improving from psychiatric symptoms is higher in younger age and advocates for a potential importance of early treatment.
Keywords: Cognitive symptoms; Endophenotype; Huntington’s disease; Psychiatric symptoms.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ghosh R, Tabrizi SJ. Clinical Aspects of Huntington’s Disease. In: Geyer MA, Ellenbroek BA, Marsden CA, Barnes TRE, Nguyen HHP, Cenci MA, editors. Behavioral Neurobiology of Huntington’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease. Berlin: Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 2013. p. 3–31.
-
- Vinther-Jensen T, Nielsen TT, Budtz-Jørgensen E, Larsen IU, Hansen MM, Hasholt L, et al. Psychiatric and cognitive symptoms in Huntington’s disease are modified by polymorphisms in catecholamine regulating enzyme genes. Clin Genet. 2016;89(3):320–7. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26081309. - PubMed
-
- Ross CA, Aylward EH, Wild EJ, Langbehn DR, Long JD, Warner JH, et al. Huntington disease: natural history, biomarkers and prospects for therapeutics. Nat Publ Gr. 2014;10(1110):204–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

