The role of personality, social economic and prevention strategy effects on health-related quality of life among people living with HIV/AIDS
- PMID: 34344462
- PMCID: PMC8336408
- DOI: 10.1186/s40249-021-00890-9
The role of personality, social economic and prevention strategy effects on health-related quality of life among people living with HIV/AIDS
Erratum in
-
Correction to: The role of personality, social economic and prevention strategy effects on health-related quality of life among people living with HIV/AIDS.Infect Dis Poverty. 2021 Sep 1;10(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s40249-021-00899-0. Infect Dis Poverty. 2021. PMID: 34470651 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: HIV/AIDS has transformed into a chronic controllable but not yet curable infectious disease as other chronic diseases to some extent. The additional of so called fourth 90% that included the improved health-related quality of life (HRQoL) for people living with HIV (PLWHIV) required solutions beyond antiretroviral therapy and viral load suppression. This study will explore the role of personality, social economic and prevention strategy effection on HRQoL among people living with HIV/AIDS.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted among PLWHIV aged more than 16 years old in the 10 municipalities in Yunnan Province, China from October 2019 to May 2020, enrolling total 1997 participants. Individual-level HRQoL data were measured by 12-item Short Form Health Survey (SF-12) and EuroQol Five Dimensions Questionnaire (EQ-5D-5L). We assembled municipal-level data about social economic from Yunnan Statistical Yearbook in 2020 and strategy practice information from the self-evaluation system. We used the principal component analysis to build the social economic and strategy effect on each area respectively and one-way ANOVA was used to perform univariate analysis to identify the predictors with significant differences. Finally we used multi-level model (MLM) to explore the personality, social economic and strategy effects in health-related quality of life among PLWHIV.
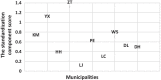
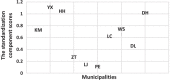
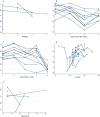
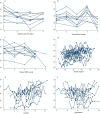
Results: The global score for quality of life measured using EQ-5D-5L had an estimated mean score (standard deviation, SD) of 0.901 ± 0.146. The HRQoL score measured using PCS-12 had an estimated mean score (SD) of 46.62 ± 8.55. The mean MCS-12 score (SD) was estimated to be 47.80 ± 9.71. The area-level predictors explained a proportion of 13.6-17.2% for the between-area variation of the HRQoL scores, regardless of the total HRQoL, physical component and mental component. The impacts of stigma (P < 0.01), social support (P < 0.001), anxiety (P < 0.001), depression (P < 0.05) and social economic status (P < 0.05) on HRQoL at the individual-level were significantly different. The plots visualized the impact of individual-level factors on a respondent's HRQoL was modified by the area-level characteristics.
Conclusions: The study identified the possible strategy determinant of individual HRQoL of PLWHIV and also the area effect on HRQoL. Stigma, social support, anxiety, depression and social economic status were the individual-level determinants on HRQoL. These could be a valuable resource for evaluating the overall health of the areas and help improve local decision making.
Keywords: HIV/AIDS; Health-related quality of life; Multi-level model; Personality factor; Prevention strategy; Social economic.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Health utility measurement for people living with HIV/AIDS under combined antiretroviral therapy: A comparison of EQ-5D-5L and SF-6D.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Nov 11;101(45):e31666. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031666. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36397330 Free PMC article.
-
Health-related quality of life in pregnant women living with HIV: a comparison of EQ-5D and SF-12.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2017 Aug 30;15(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s12955-017-0731-8. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2017. PMID: 28851384 Free PMC article.
-
Health-related quality of life and its predictors among adults living with HIV/AIDS and receiving antiretroviral therapy in Pakistan.Qual Life Res. 2021 Jun;30(6):1653-1664. doi: 10.1007/s11136-021-02771-y. Epub 2021 Feb 13. Qual Life Res. 2021. PMID: 33582967 Free PMC article.
-
Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients With Different Diseases Measured With the EQ-5D-5L: A Systematic Review.Front Public Health. 2021 Jun 29;9:675523. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.675523. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34268287 Free PMC article.
-
Health-Related Quality of Life Among Patients Who Have Survived an Episode of Sepsis in the United States: A Systematic Review.Infect Dis Ther. 2025 Feb;14(2):385-400. doi: 10.1007/s40121-024-01106-x. Epub 2025 Jan 25. Infect Dis Ther. 2025. PMID: 39862376 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Predictors of an Active Lifestyle in Middle-Aged and Older Adults with HIV in the United States Deep South.HIV AIDS (Auckl). 2023 Mar 2;15:63-70. doi: 10.2147/HIV.S399842. eCollection 2023. HIV AIDS (Auckl). 2023. PMID: 36891235 Free PMC article.
-
An international compendium of health state utilities in people with HIV: a systematic review.Qual Life Res. 2025 Apr 17. doi: 10.1007/s11136-025-03966-3. Online ahead of print. Qual Life Res. 2025. PMID: 40246804 Review.
-
Health-related quality of life of Chinese AIDS patients: a multi-region study.Qual Life Res. 2023 Apr;32(4):1005-1014. doi: 10.1007/s11136-022-03299-5. Epub 2022 Nov 22. Qual Life Res. 2023. PMID: 36417088
-
Income in Relation to Psychosocial Factors Among Stroke Survivors using Smartwatches for Atrial Fibrillation Monitoring.Cardiol Cardiovasc Med. 2024;8(5):433-439. doi: 10.26502/fccm.92920404. Epub 2024 Oct 11. Cardiol Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39493359 Free PMC article.
-
State of mental health, sleep status, and the interaction with health-related quality of life in HIV-infected Chinese patients during the COVID-19 pandemic.BMC Public Health. 2024 May 30;24(1):1445. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18929-5. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38816790 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Emily F, Thomas R, Anke S, Katrin W, Petra K. Health-related quality of life in overweight German children and adolescents: do treatment-seeking youth have low-quality of life levels? Comparison of a clinical sample with the general population using a multilevel model approach. BMC Public Health. 2013;13:561. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-13-561. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

