CXCL16 Promotes Gastric Cancer Tumorigenesis via ADAM10-Dependent CXCL16/CXCR6 Axis and Activates Akt and MAPK Signaling Pathways
- PMID: 34345211
- PMCID: PMC8326113
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.57826
CXCL16 Promotes Gastric Cancer Tumorigenesis via ADAM10-Dependent CXCL16/CXCR6 Axis and Activates Akt and MAPK Signaling Pathways
Erratum in
-
Erratum: CXCL16 Promotes Gastric Cancer Tumorigenesis via ADAM10-Dependent CXCL16/CXCR6 Axis and Activates Akt and MAPK Signaling Pathways: Erratum.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Jun 21;19(10):3285-3287. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.84342. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37416762 Free PMC article.
Abstract
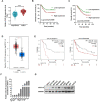
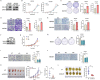
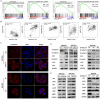
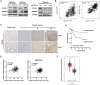
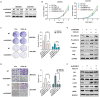
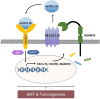
Abnormal expression of CXC motif chemokine ligand 16 (CXCL16) has been demonstrated to be associated with tumor progression and metastasis, served as a prognostic factor in many cancers, with higher relative expression behaving as a marker of tumor progression. However, its role and mechanisms underlying progression and metastasis of gastric cancer (GC) are yet to be elucidated. In our investigation, public datasets and human GC tissue samples were used to determine the CXCL16 expression levels. Our results revealed that CXCL16 was upregulated in GC. The high expression CXCL16 in GC was significantly associated with histologic poor differentiation and pTNM staging. And high CXCL16 was positively correlated with the poor survival of GC patients. Gain-and loss-of-function experiments were employed to investigate the biological role of CXCL16 in proliferation and migration both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanically, Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) revealed that the epithelial‑mesenchymal transition (EMT), Akt and MAPK signal pathway related genes were significantly enriched in the high CXCL16 group, which was confirmed by western blot. Moreover, overexpression CXCL16 promoted the disintegrin and metalloproteases (ADAM10) and the CXC motif chemokine receptor 6 (CXCR6) expression, which mediated the CXCL16/CXCR6 positive feedback loop in GC, with activating Akt and MAPK signaling pathways. Knocking down ADAM10 would interrupted the CXCL16/CXCR6 axis in the carcinogenesis and progression of GC. In conclusion, our findings offered insights into that CXCL16 promoted GC tumorigenesis by enhancing ADAM10-dependent CXCL16/CXCR6 axis activation.
Keywords: ADAM10; CXCL16; gastric cancer; tumorigenesis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I. et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Sano T. Gastric cancer: Asia and the world. Gastric Cancer. 2017;20:1–2. - PubMed
-
- Van Cutsem E, Sagaert X, Topal B. et al. Gastric cancer. Lancet. 2016;388:2654–64. - PubMed
-
- Baggiolini M. Chemokines and leukocyte traffic. Nature. 1998;392:565–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

