Effects of sodium zirconium cyclosilicate on sodium and potassium excretion in healthy adults: a Phase 1 study
- PMID: 34345416
- PMCID: PMC8323143
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfaa237
Effects of sodium zirconium cyclosilicate on sodium and potassium excretion in healthy adults: a Phase 1 study
Abstract
Background: Sodium zirconium cyclosilicate (SZC; formerly ZS-9) is a potassium (K+) binder for treatment of hyperkalemia in adults. SZC binds K+ in exchange for sodium (Na+) or hydrogen (H+) in the gastrointestinal tract, conveying potential for systemic absorption of Na+.
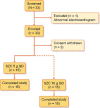
Methods: This single-center Phase 1 study evaluated the effects of SZC on Na+ and K+ excretion in healthy, normokalemic adults. During an initial run-in period (Days 1-2), participants started a high K+/low Na+ diet. After baseline (Days 3-4), SCZ 5 or 10 g once daily (QD) was administered (Days 5-8). The primary endpoint was mean change in urinary Na+ excretion from baseline (Days 3-4) to the treatment period (Days 7-8).
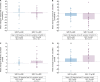
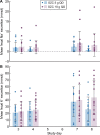
Results: Of 32 enrolled participants, 30 entered and completed the study; the first 15 received 5 g and the next 15 received 10 g. Nonsignificant changes from baseline in urinary Na+ excretion were observed with SZC 5 g (mean ± SD -0.93 ± 25.85 mmol/24 h) and 10 g (-5.47 ± 13.90 mmol/24 h). Statistically significant decreases from baseline in urinary K+ excretion (mean ± SD -21.17 ± 21.26 mmol/24 h; P = 0.0017) and serum K+ concentration (-0.25 ± 0.24 mmol/L; P = 0.0014) were observed with the 10-g dose. There were few adverse events and no clinically meaningful changes in vital signs or laboratory safety measures.
Conclusions: Treatment with SZC 5 or 10 g QD reduced serum K+ concentration and urinary K+ excretion, with no significant effect on urinary Na+ excretion, and was well tolerated.
Keywords: Phase 1 study; excretion; hyperkalemia; potassium; sodium; sodium zirconium cyclosilicate.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA.
Figures


References
-
- Kovesdy CP. Management of hyperkalaemia in chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 2014; 10: 653–662 - PubMed
-
- Linder KE, Krawczynski MA, Laskey D.. Sodium zirconium cyclosilicate (ZS-9): a novel agent for the treatment of hyperkalemia. Pharmacotherapy 2016; 36: 923–933 - PubMed
-
- Betts KA, Woolley JM, Mu F. et al. The prevalence of hyperkalemia in the United States. Curr Med Res Opin 2018; 34: 971–978 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

