Skin erosion in deep brain stimulation procedures: Using the temporalis muscle to treat this complication - A technical note
- PMID: 34345495
- PMCID: PMC8326058
- DOI: 10.25259/SNI_372_2021
Skin erosion in deep brain stimulation procedures: Using the temporalis muscle to treat this complication - A technical note
Abstract
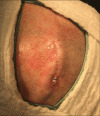
Background: Skin erosion is a common complication after deep brain stimulator procedures. Despite being a relatively common event, there is no standard surgical technique or a widely accepted guideline for managing this kind of complication.
Methods: We describe a case of cutaneous erosion in the connector's site of deep brain stimulation case, surgically managed with anterior displacement of the connectors and overlapping and wrapping the connections within the temporal muscle.
Results: Postoperatively, the patient did well and achieved complete resolution of the skin erosion, with no signs of infection or new skin lesions.
Conclusion: This technique demonstrated to be effective in this case in the long-term follow-up.
Keywords: Complications; Deep brain stimulation; Functional neurosurgery; Parkinson’s disease; Skin erosion.
Copyright: © 2021 Surgical Neurology International.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Aum DJ, Tierney TS. Deep brain stimulation: Foundations and future trends. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2018;23:162–82. - PubMed
-
- Bakhsheshian J, Dahdaleh NS, Lam SK, Savage JW, Smith ZA. The use of vancomycin powder in modern spine surgery: Systematic review and meta-analysis of the clinical evidence. World Neurosurg. 2015;83:816–23. - PubMed
-
- Barrett TF, Rasouli JJ, Taub P, Kopell BH. Technical note: Preemptive surgical revision of impending deep brain stimulation hardware erosion. World Neurosurg. 2018;111:41–6. - PubMed
-
- Beitz JM. Parkinson’s disease: A review. Front Biosci. 2014;6:65–74. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
