The Diagnosis and Management of Pediatric Spine Infections
- PMID: 34345570
- PMCID: PMC8323075
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.16748
The Diagnosis and Management of Pediatric Spine Infections
Abstract
The management of pediatric spine infections requires a multidisciplinary approach that includes orthopedic surgeons, infectious disease specialists, interventional radiologists, and others. The prevalence of the disease has increased in frequency, virulence, and degree of soft tissue involvement over the past several years; there has also been a resurgence of some types of infections, such as tuberculosis, fungal, and viral pathogens. The diagnosis can often be reached with a detailed history, physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Pathologies mimicking infection require a more invasive approach for diagnosis, including core or open biopsy. The treatment of discitis, spondylodiscitis, vertebral osteomyelitis, spinal epidural, and intramedullary abscesses in children is at times complex, and although many infections can be treated non-surgically with antibiotic therapy, some more extensive infections require surgical management. A timely diagnosis is important as it allows the initiation of the appropriate antimicrobial therapy and would decrease the complexity of the subsequent surgical intervention.
Keywords: ct-guided biopsy; epidural abscess; spondylodiscitis; tubercular osteomyelitis; vertebral osteomyelitis.
Copyright © 2021, Saleh et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



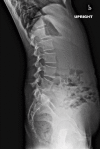

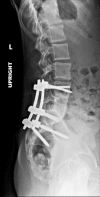
References
-
- Spinal infections in children: a multicentre retrospective study. Dayer R, Alzahrani MM, Saran N, et al. Bone Joint J. 2018;100-B:542–548. - PubMed
-
- Paediatric spondylodiscitis: a 10-year single institution experience in management and clinical outcomes. Afshari FT, Rodrigues D, Bhat M, Solanki GA, Walsh AR, Lo WB. Childs Nerv Syst. 2020;36:1049–1054. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
