Interleukin-7 Reverses Lymphopenia and Improves T-Cell Function in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patient With Inborn Error of Toll-Like Receptor 3: A Case Report
- PMID: 34345826
- PMCID: PMC8322565
- DOI: 10.1097/CCE.0000000000000500
Interleukin-7 Reverses Lymphopenia and Improves T-Cell Function in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patient With Inborn Error of Toll-Like Receptor 3: A Case Report
Abstract
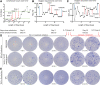
Background: Immunotherapy treatment for coronavirus disease 2019 combined with antiviral therapy and supportive care remains under intense investigation. However, the capacity to distinguish patients who would benefit from immunosuppressive or immune stimulatory therapies remains insufficient. Here, we present a patient with severe coronavirus disease 2019 with a defective immune response, treated successfully with interleukin-7 on compassionate basis with resultant improved adaptive immune function.
Case summary: A previously healthy 43-year-old male developed severe acute respiratory distress syndrome due to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 virus with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure and persistent, profound lymphopenia. Functional analysis demonstrated depressed lymphocyte function and few antigen-specific T cells. Interleukin-7 administration resulted in reversal of lymphopenia and improved T-cell function. Respiratory function and clinical status rapidly improved, and he was discharged home. Whole exome sequencing identified a deleterious autosomal dominant mutation in TICAM1, associated with a dysfunctional type I interferon antiviral response with increased severity of coronavirus disease 2019 disease.
Conclusions: Immunoadjuvant therapies to boost host immunity may be efficacious in life-threatening severe coronavirus disease 2019 infections, particularly by applying a precision medicine approach in selecting patients expressing an immunosuppressive phenotype.
Keywords: case report; coronavirus disease 2019; immunotherapy; interferons; interleukin-7; toll-like receptor 3.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Turnbull has received funding from the National Institute of Health (NIH), National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS) GM133756. Dr. Morre is chief scientist for RevImmune, the company that generously provided interleukin-7 for this patient. Dr. Moldawer has received funding from the NIH, NIGMS GM139046. Dr. Di Paola has received funding from the NIH, National Heart, Lung, Blood Institute HL139825. Dr. Hotchkiss has received funding from the NIH, NIGMS GM126928. Dr. Remy has received funding from the NIH, NIGMS GM129763, and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences UL1TR0002345. The remaining authors have disclosed that they do not have any conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

