Design and synthesis of a new orthogonally protected glutamic acid analog and its use in the preparation of high affinity polo-like kinase 1 polo-box domain - binding peptide macrocycles
- PMID: 34346472
- PMCID: PMC8456285
- DOI: 10.1039/d1ob01120k
Design and synthesis of a new orthogonally protected glutamic acid analog and its use in the preparation of high affinity polo-like kinase 1 polo-box domain - binding peptide macrocycles
Abstract
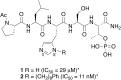
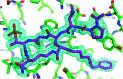
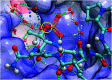
Targeting protein - protein interactions (PPIs) has emerged as an important area of discovery for anticancer therapeutic development. In the case of phospho-dependent PPIs, such as the polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) polo-box domain (PBD), a phosphorylated protein residue can provide high-affinity recognition and binding to target protein hot spots. Developing antagonists of the Plk1 PBD can be particularly challenging if one relies solely on interactions within and proximal to the phospho-binding pocket. Fortunately, the affinity of phospho-dependent PPI antagonists can be significantly enhanced by taking advantage of interactions in both the phospho-binding site and hidden "cryptic" pockets that may be revealed on ligand binding. In our current paper, we describe the design and synthesis of macrocyclic peptide mimetics directed against the Plk1 PBD, which are characterized by a new glutamic acid analog that simultaneously serves as a ring-closing junction that provides accesses to a cryptic binding pocket, while at the same time achieving proper orientation of a phosphothreonine (pT) residue for optimal interaction in the signature phospho-binding pocket. Macrocycles prepared with this new amino acid analog introduce additional hydrogen-bonding interactions not found in the open-chain linear parent peptide. It is noteworthy that this new glutamic acid-based amino acid analog represents the first example of extremely high affinity ligands where access to the cryptic pocket from the pT-2 position is made possible with a residue that is not based on histidine. The concepts employed in the design and synthesis of these new macrocyclic peptide mimetics should be useful for further studies directed against the Plk1 PBD and potentially for ligands directed against other PPI targets.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Fine-tuning probes for fluorescence polarization binding assays of bivalent ligands against polo-like kinase 1 using full-length protein.Bioorg Med Chem. 2025 Mar 1;119:118055. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2024.118055. Epub 2024 Dec 28. Bioorg Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39764864 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Highly Selective 1,2,3-Triazole-containing Peptidic Polo-like Kinase 1 Polo-box Domain-binding Inhibitors.Molecules. 2019 Apr 16;24(8):1488. doi: 10.3390/molecules24081488. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31014020 Free PMC article.
-
Histidine N(τ)-cyclized macrocycles as a new genre of polo-like kinase 1 polo-box domain-binding inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2018 Oct 15;28(19):3202-3205. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.08.018. Epub 2018 Aug 19. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2018. PMID: 30174151 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and enzoinformatics perspectives of targeting Polo-like kinase 1 in cancer therapy.Semin Cancer Biol. 2019 Jun;56:47-55. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.11.004. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Semin Cancer Biol. 2019. PMID: 29122685 Review.
-
[Mining Polo-Box domain of Polo-like kinase 1 as a new therapeutic target for cancer].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2020 Nov 25;36(11):2298-2312. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.200132. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2020. PMID: 33244925 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Fine-tuning probes for fluorescence polarization binding assays of bivalent ligands against polo-like kinase 1 using full-length protein.Bioorg Med Chem. 2025 Mar 1;119:118055. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2024.118055. Epub 2024 Dec 28. Bioorg Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39764864 Free PMC article.
-
Affinity enhancement of polo-like kinase 1 polo box domain-binding ligands by a bivalent approach using a covalent kinase-binding component.RSC Chem Biol. 2024 Jun 4;5(8):721-728. doi: 10.1039/d4cb00031e. eCollection 2024 Jul 31. RSC Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 39092437 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomimetics of Natural Regulators of JAK-STAT Pathway: Novel Therapeutic Perspectives.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Jan 3;8:792546. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.792546. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35047557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Polo-Like Kinase 1 in Regulating the Forkhead Box Family Transcription Factors.Cells. 2023 May 8;12(9):1344. doi: 10.3390/cells12091344. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37174744 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rolland T. Taşan M. Charloteaux B. Pevzner S. J. Zhong Q. Sahni N. Yi S. Lemmens I. Fontanillo C. Mosca R. Kamburov A. Ghiassian S. D. Yang X. Ghamsari L. Balcha D. Begg B. E. Braun P. Brehme M. Broly M. P. Carvunis A.-R. Convery-Zupan D. Corominas R. Coulombe-Huntington J. Dann E. Dreze M. Dricot A. Fan C. Franzosa E. Gebreab F. Gutierrez B. J. Hardy M. F. Jin M. Kang S. Kiros R. Lin G. N. Luck K. MacWilliams A. Menche J. Murray R. R. Palagi A. Poulin M. M. Rambout X. Rasla J. Reichert P. Romero V. Ruyssinck E. Sahalie J. M. Scholz A. Shah A. A. Sharma A. Shen Y. Spirohn K. Tam S. Tejeda A. O. Trigg S. A. Twizere J.-C. Vega K. Walsh J. Cusick M. E. Xia Y. Barabási A.-L. Iakoucheva L. M. Aloy P. De Las Rivas J. Tavernier J. Calderwood M. A. Hill D. E. Hao T. Roth F. P. Vidal M. Cell. 2014;159:1212–1226. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.10.050. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

