Lapatinib and poziotinib overcome ABCB1-mediated paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer
- PMID: 34347777
- PMCID: PMC8336885
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0254205
Lapatinib and poziotinib overcome ABCB1-mediated paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer
Abstract
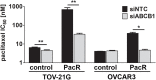
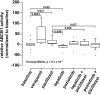
Conventional frontline treatment for ovarian cancer consists of successive chemotherapy cycles of paclitaxel and platinum. Despite the initial favorable responses for most patients, chemotherapy resistance frequently leads to recurrent or refractory disease. New treatment strategies that circumvent or prevent mechanisms of resistance are needed to improve ovarian cancer therapy. We established in vitro paclitaxel-resistant ovarian cancer cell line and organoid models. Gene expression differences in resistant and sensitive lines were analyzed by RNA sequencing. We manipulated candidate genes associated with paclitaxel resistance using siRNA or small molecule inhibitors, and then screened the cells for paclitaxel sensitivity using cell viability assays. We used the Bliss independence model to evaluate the anti-proliferative synergy for drug combinations. ABCB1 expression was upregulated in paclitaxel-resistant TOV-21G (q < 1x10-300), OVCAR3 (q = 7.4x10-156) and novel ovarian tumor organoid (p = 2.4x10-4) models. Previous reports have shown some tyrosine kinase inhibitors can inhibit ABCB1 function. We tested a panel of tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the ability to sensitize resistant ABCB1-overexpressing ovarian cancer cell lines to paclitaxel. We observed synergy when we combined poziotinib or lapatinib with paclitaxel in resistant TOV-21G and OVCAR3 cells. Silencing ABCB1 expression in paclitaxel-resistant TOV-21G and OVCAR3 cells reduced paclitaxel IC50 by 20.7 and 6.2-fold, respectively. Furthermore, we demonstrated direct inhibition of paclitaxel-induced ABCB1 transporter activity by both lapatinib and poziotinib. In conclusion, lapatinib and poziotinib combined with paclitaxel synergizes to inhibit the proliferation of ABCB1-overexpressing ovarian cancer cells in vitro. The addition of FDA-approved lapatinib to second-line paclitaxel therapy is a promising strategy for patients with recurrent ovarian cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



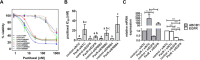
References
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Statistics Center—Ovary 2018 [cited 2020 April 13]. Available from: https://cancerstatisticscenter.cancer.org/#!/cancer-site/Ovary.
-
- Ozols RF, Bundy BN, Greer BE, Fowler JM, Clarke-Pearson D, Burger RA, et al. Phase III trial of carboplatin and paclitaxel compared with cisplatin and paclitaxel in patients with optimally resected stage III ovarian cancer: a Gynecologic Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21(17):3194–200. Epub 2003/07/16. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2003.02.153 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Piccart MJ, Bertelsen K, James K, Cassidy J, Mangioni C, Simonsen E, et al. Randomized intergroup trial of cisplatin-paclitaxel versus cisplatin-cyclophosphamide in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer: three-year results. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92(9):699–708. Epub 2000/05/04. doi: 10.1093/jnci/92.9.699 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

