The COVIDome Explorer researcher portal
- PMID: 34348131
- PMCID: PMC8316015
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109527
The COVIDome Explorer researcher portal
Abstract
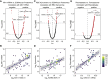
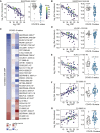
COVID-19 pathology involves dysregulation of diverse molecular, cellular, and physiological processes. To expedite integrated and collaborative COVID-19 research, we completed multi-omics analysis of hospitalized COVID-19 patients, including matched analysis of the whole-blood transcriptome, plasma proteomics with two complementary platforms, cytokine profiling, plasma and red blood cell metabolomics, deep immune cell phenotyping by mass cytometry, and clinical data annotation. We refer to this multidimensional dataset as the COVIDome. We then created the COVIDome Explorer, an online researcher portal where the data can be analyzed and visualized in real time. We illustrate herein the use of the COVIDome dataset through a multi-omics analysis of biosignatures associated with C-reactive protein (CRP), an established marker of poor prognosis in COVID-19, revealing associations between CRP levels and damage-associated molecular patterns, depletion of protective serpins, and mitochondrial metabolism dysregulation. We expect that the COVIDome Explorer will rapidly accelerate data sharing, hypothesis testing, and discoveries worldwide.
Keywords: COVID-19; CRP; SARS; data portal; immune system; infection; inflammation; metabolism; multi-omics; serpins.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests J.M.E. serves in the COVID Development Advisory Board for Elly Lilly and has provided consulting services to Gilead Sciences Inc. J.M.E. also serves on the Cell Reports Advisory Board. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Update of
-
The COVIDome Explorer Researcher Portal.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Mar 8:2021.03.04.21252945. doi: 10.1101/2021.03.04.21252945. medRxiv. 2021. Update in: Cell Rep. 2021 Aug 17;36(7):109527. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109527. PMID: 33758879 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

