New Parameter of the Second Half of the P-Wave, P-Wave Duration, and Atrial Conduction Times Predict Atrial Fibrillation during Electrophysiological Studies
- PMID: 34348309
- PMCID: PMC8562052
- DOI: 10.1159/000518262
New Parameter of the Second Half of the P-Wave, P-Wave Duration, and Atrial Conduction Times Predict Atrial Fibrillation during Electrophysiological Studies
Abstract
Objective: Several P-wave parameters reflect atrial conduction characteristics and have been used to predict atrial fibrillation (AF). The aim of this study was to determine the relationship between maximum P-wave duration (PMax) and new P-wave parameters, with atrial conduction times (CT), and to assess their predictive value of AF during electrophysiological studies (AF-EPS).
Subjects and methods: This was a cross-sectional study in 153 randomly selected patients aged 18-70 years, undergoing EPS. The patients were divided into 2 groups designated as no AF-EPS and AF-EPS, depending on whether AF occurred during EPS or not. Different P-wave parameters and atrial CT were compared for both study groups. Subsequently, the predictive value of the P-wave parameters and the atrial CT for AF-EPS was evaluated.
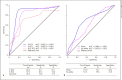
Results: The values of CT, PMax, and maximum Ppeak-Pend interval (Pp-eMax) were significantly higher in patients with AF-EPS. Almost all P-wave parameters were correlated with the left CT. PMax, Pp-eMax, and CT were univariate and multivariate predictors of AF-EPS. The largest ROC area was presented by interatrial CT (0.852; p < 0.001; cutoff value: ≥82.5 ms; sensitivity: 91.1%; specificity: 81.1%). Pp-eMax showed greater sensitivity (79.5%) to discriminate AF-EPS than PMax (72.7%), but the latter had better specificity (60.4% vs. 41.5%).
Conclusions: Left atrial CT were directly and significantly correlated with PMax and almost all the parameters of the second half of the P-wave. CT, PMax, and Pp-eMax (new parameter) were good predictors of AF-EPS, although CT did more robustly.
Keywords: Atrial conduction time; Atrial fibrillation; Electrocardiogram; Electrophysiological study; P-wave.
© 2021 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Chen Q, Gasperetti A, Della Rocca DG, Mohanty S, Gedikli O, Trivedi C, et al. The value of baseline and arrhythmic ECG in the interpretation of arrhythmic mechanisms. Card Electrophysiol Clin. 2019;11:219–38. - PubMed
-
- Carmona Puerta R, Lorenzo Martínez E. P wave dispersion over two decades after its discovery. What the cardiologist should know. CardioClinics. 2021;56((1)):49–57.
-
- Platonov PG. Atrial conduction and atrial fibrillation: what can we learn from surface ECG? Cardiol J. 2008;15:402–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

