Obesity is associated with severe disease and mortality in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis
- PMID: 34348687
- PMCID: PMC8334342
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-021-11546-6
Obesity is associated with severe disease and mortality in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has led to global research to predict those who are at greatest risk of developing severe disease and mortality. The aim of this meta-analysis was to determine the associations between obesity and the severity of and mortality due to COVID-19.
Methods: We searched the PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library and Web of Science databases for studies evaluating the associations of obesity with COVID-19. Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using random- or fixed-effects models. Meta-regression analyses were conducted to estimate regression coefficients.
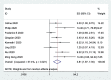
Results: Forty-six studies involving 625,153 patients were included. Compared with nonobese patients, obese patients had a significantly increased risk of infection. (OR 2.73, 95% CI 1.53-4.87; I2 = 96.8%), hospitalization (OR 1.72, 95% CI 1.55-1.92; I2 = 47.4%), clinically severe disease (OR 3.81, 95% CI 1.97-7.35; I2 = 57.4%), mechanical ventilation (OR 1.66, 95% CI 1.42-1.94; I2 = 41.3%), intensive care unit (ICU) admission (OR 2.25, 95% CI 1.55-3.27; I2 = 71.5%), and mortality (OR 1.61, 95% CI 1.29-2.01; I2 = 83.1%).
Conclusion: Patients with obesity may have a greater risk of infection, hospitalization, clinically severe disease, mechanical ventilation, ICU admission, and mortality due to COVID-19. Therefore, it is important to increase awareness of these associations with obesity in COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: COVID-19; Mortality; Obesity; Predict; Severity.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, Cheng Z, Yu T, Xia J, Wei Y, Wu W, Xie X, Yin W, Li H, Liu M, Xiao Y, Gao H, Guo L, Xie J, Wang G, Jiang R, Gao Z, Jin Q, Wang J, Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):497–506. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

