Immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in Dialysis
- PMID: 34348908
- PMCID: PMC8806103
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2021040432
Immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in Dialysis
Abstract
Background: Patients receiving maintenance dialysis represent a high-risk, immune-compromised population with 15%-25% COVID-19 mortality rate who were unrepresented in clinical trials of mRNA vaccines.
Methods: All patients receiving maintenance dialysis who received two doses of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines with antibody test results drawn ≥14 days after the second dose, as documented in the electronic health record through March 18, 2021, were included. Response was on the basis of levels of Ig-G against the receptor binding domain of the S1 subunit of SARS-CoV-2 spike-antigen (seropositive ≥2 U/L) using an FDA-approved semiquantitative chemiluminescent assay (ADVIA Centaur XP/XPT COV2G).
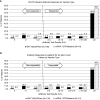
Results: Among 186 patients on dialysis from 30 clinics in eight states tested 23±8 days after receiving two vaccine doses, there were 165 (88.7%) responders with 70% at maximum titer. There was no significant difference between BNT162b2/Pfizer (148 out of 168, 88.1%) and mRNA-1273/Moderna (17 out of 18, 94.4%), P=0.42. All 38 patients with COVID-19 history were responders, with 97% at maximum titer. Among patients without COVID-19, 127 out of 148 (85.8%) were responders, comparable between BNT162b2/Pfizer (113 out of 133) and mRNA-1273/Moderna (14 out of 15) vaccines (85.0% versus 93.3%, P=0.38).
Conclusions: Most patients receiving maintenance dialysis responded after two doses of BNT162b2/Pfizer or mRNA-1273/Moderna vaccine, suggesting the short-term development of antispike antibody is good, giving hope that most of these patients who are vulnerable, once immunized, will be protected from COVID-19. Longer-term evaluation is needed to determine antibody titer durability and if booster dose(s) are warranted. Further research to evaluate the approach to patients without a serologic response is needed, including benefits of additional dose(s) or administration of alternate options.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; chronic kidney disease; clinical immunology; dialysis; end-stage kidney disease; immune deficiency; vaccine.
Copyright © 2021 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
Update of
-
Immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in Dialysis.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Apr 13:2021.04.08.21254779. doi: 10.1101/2021.04.08.21254779. medRxiv. 2021. Update in: J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021 Nov;32(11):2735-2742. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2021040432. PMID: 33880482 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- United States Renal Data System : 2020 USRDS Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States, Bethesda, MD, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2020. Available at: https://adr.usrds.org/2020/end-stage-renal-disease/1-incidence-prevalenc.... Accessed September 29, 2021
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous