Delineating virulence of Vibrio campbellii: a predominant luminescent bacterial pathogen in Indian shrimp hatcheries
- PMID: 34349168
- PMCID: PMC8339124
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-94961-4
Delineating virulence of Vibrio campbellii: a predominant luminescent bacterial pathogen in Indian shrimp hatcheries
Abstract
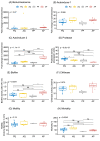
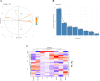
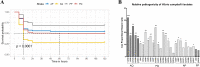
Luminescent vibriosis is a major bacterial disease in shrimp hatcheries and causes up to 100% mortality in larval stages of penaeid shrimps. We investigated the virulence factors and genetic identity of 29 luminescent Vibrio isolates from Indian shrimp hatcheries and farms, which were earlier presumed as Vibrio harveyi. Haemolysin gene-based species-specific multiplex PCR and phylogenetic analysis of rpoD and toxR identified all the isolates as V. campbellii. The gene-specific PCR revealed the presence of virulence markers involved in quorum sensing (luxM, luxS, cqsA), motility (flaA, lafA), toxin (hly, chiA, serine protease, metalloprotease), and virulence regulators (toxR, luxR) in all the isolates. The deduced amino acid sequence analysis of virulence regulator ToxR suggested four variants, namely A123Q150 (AQ; 18.9%), P123Q150 (PQ; 54.1%), A123P150 (AP; 21.6%), and P123P150 (PP; 5.4% isolates) based on amino acid at 123rd (proline or alanine) and 150th (glutamine or proline) positions. A significantly higher level of the quorum-sensing signal, autoinducer-2 (AI-2, p = 2.2e-12), and significantly reduced protease activity (p = 1.6e-07) were recorded in AP variant, whereas an inverse trend was noticed in the Q150 variants AQ and PQ. The pathogenicity study in Penaeus (Litopenaeus) vannamei juveniles revealed that all the isolates of AQ were highly pathogenic with Cox proportional hazard ratio 15.1 to 32.4 compared to P150 variants; PP (5.4 to 6.3) or AP (7.3 to 14). The correlation matrix suggested that protease, a metalloprotease, was positively correlated with pathogenicity (p > 0.05) and negatively correlated (p < 0.05) with AI-2 and AI-1. The syntenic organization of toxS-toxR-htpG operon in V. campbellii was found to be similar to pathogenic V. cholerae suggesting a similar regulatory role. The present study emphasizes that V. campbellii is a predominant pathogen in Indian shrimp hatcheries, and ToxR plays a significant role as a virulence regulator in the quorum sensing-protease pathway. Further, the study suggests that the presence of glutamine at 150th position (Q150) in ToxR is crucial for the pathogenicity of V. campbellii.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Tacon AGJ. Trends in global aquaculture and aquafeed production: 2000–2017. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020;28:43–56. doi: 10.1080/23308249.2019.1649634. - DOI
-
- Chrisolite B, et al. Distribution of luminescent Vibrio harveyi and their bacteriophages in a commercial shrimp hatchery in South India. Aquaculture. 2008;275:13–19. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.12.016. - DOI
-
- Karunasagar I, Pai R, Malathi GR, Karunasagar I. Mass mortality of Penaeus monodon larvae due to antibiotic-resistant Vibrio harveyi infection. Aquaculture. 1994;128:203–209. doi: 10.1016/0044-8486(94)90309-3. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

