Effect of erythritol and xylitol on Streptococcus pyogenes causing peritonsillar abscesses
- PMID: 34349211
- PMCID: PMC8339055
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-95367-y
Effect of erythritol and xylitol on Streptococcus pyogenes causing peritonsillar abscesses
Abstract
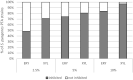
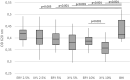
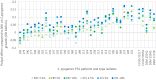
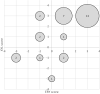
Polyols are effective against caries-causing streptococci but the effect on oropharynx-derived pyogenic streptococci is not well characterised. We aimed to study the effect of erythritol (ERY) and xylitol (XYL) against Streptococcus pyogenes isolated from peritonsillar abscesses (PTA). We used 31 clinical isolates and 5 throat culture collection strains. Inhibition of bacterial growth by polyols at 2.5%, 5% and 10% concentrations was studied and the results were scored. Amylase levels in PTA pus were compared to polyol effectivity scores (PES). Growth curves of four S. pyogenes isolates were analysed. Our study showed that XYL was more effective than ERY inhibiting 71-97% and 48-84% of isolates, respectively, depending of concentrations. 48% of clinical and all throat strains were inhibited by polyols in all concentrations (PES 3). PES was negative or zero in 26% of the isolates in the presence of ERY and in 19% of XYL. ERY enhanced the growth of S. pyogenes isolated from pus with high amylase levels. Polyols in all concentrations inhibited the growth in exponential phase. In conclusion, ERY and XYL are potent growth inhibitors of S. pyogenes isolated from PTA. Therefore, ERY and XYL may have potential in preventing PTA in the patients with frequent tonsillitis episodes.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Anirikh Chakrabarti was employed by Cargill during the preparation of this manuscript, and Cargill produced erythritol. The rest of the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
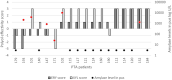
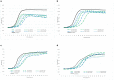
Similar articles
-
Xylitol and erythritol decrease adherence of polysaccharide-producing oral streptococci.Curr Microbiol. 2010 Jan;60(1):25-9. doi: 10.1007/s00284-009-9496-6. Epub 2009 Sep 24. Curr Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 19777305
-
Exploration of singular and synergistic effect of xylitol and erythritol on causative agents of dental caries.Sci Rep. 2020 Apr 14;10(1):6297. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63153-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32286378 Free PMC article.
-
Peritonsillar abscess: clinical aspects of microbiology, risk factors, and the association with parapharyngeal abscess.Dan Med J. 2017 Mar;64(3):B5333. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28260599 Review.
-
Peritonsillar abscess may not always be a complication of acute tonsillitis: A prospective cohort study.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 3;15(4):e0228122. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228122. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32243441 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic effects of the natural sweeteners xylitol and erythritol: A comprehensive review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020;60(12):1986-1998. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2019.1623757. Epub 2019 Jun 16. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020. PMID: 31204494 Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the etiology of peritonsillar abscess using next generation sequencing.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2023 Nov 8;22(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s12941-023-00649-0. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2023. PMID: 37940951 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Passy V. Pathogenesis of peritonsillar abscess. Laryngoscope. 1994;104(2):185–190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

