Establishment of human airway epithelial cells with doxycycline-inducible cell growth and fluorescence reporters
- PMID: 34349346
- PMCID: PMC8319267
- DOI: 10.1007/s10616-021-00477-0
Establishment of human airway epithelial cells with doxycycline-inducible cell growth and fluorescence reporters
Abstract
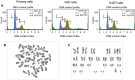
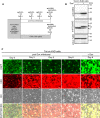
We previously reported the successful establishment of multiple immortalized cell lines that preserved the original nature of the primary cells via co-expression of R24C mutant cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4R24C), Cyclin D1, and telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT). However, as these genes are kind of oncogenes, tools to control their expression levels are favorable. In this study, we describe a new polycistronic lentiviral vector expressing proliferation factors, CDK4R24C and Cyclin D1 along with enhanced green fluorescence protein (EGFP) under the control of doxycycline (Dox)-dependent transactivator (rtTA) and tetracycline response element (TRE). By introducing the Dox-inducible lentiviral vector into human airway epithelial cells, we established a novel human airway epithelial cell line harboring polycistronic Dox-inducible CDK4R24C and Cyclin D1, referred to as Tet-on K4D cells. We showed that the cell growth of Tet-on K4D cells could be controlled by Dox. Furthermore, expression of K4D genes and rtTA gene can be independently monitored by fluorescent imaging. Cultured airway epithelial cells are useful as a tool for studying the pathogenesis of lung disorders. Altogether, our established human airway epithelial cells could be used for a variety of studies such as lung pathology and biology underlying the differentiation process to form the complex pseudostratified multicellular layers.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s10616-021-00477-0.
Keywords: CDK4R24C; Cyclin D1; Doxycycline-inducible lentiviral system; Fluorescence reporters human airway epithelial cells.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V. 2021.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Controlled cell proliferation and immortalization of human dental pulp stem cells with a doxycycline-inducible expression system.Cell Biochem Funct. 2024 Jun;42(4):e4064. doi: 10.1002/cbf.4064. Cell Biochem Funct. 2024. PMID: 38807466
-
Immortalized Canine Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells as a Novel Candidate Cell Source for Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 23;24(3):2250. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032250. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768587 Free PMC article.
-
Generation and Characterization of Inducible Lung and Skin-Specific IL-22 Transgenic Mice.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2223:115-132. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1001-5_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33226591
-
Tet-On Systems For Doxycycline-inducible Gene Expression.Curr Gene Ther. 2016;16(3):156-67. doi: 10.2174/1566523216666160524144041. Curr Gene Ther. 2016. PMID: 27216914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fish cell line: depositories, web resources and future applications.Cytotechnology. 2024 Feb;76(1):1-25. doi: 10.1007/s10616-023-00601-2. Epub 2023 Nov 27. Cytotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38304629 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

