Astaxanthin Inhibits Interleukin-6 Expression in Cerulein/Resistin-Stimulated Pancreatic Acinar Cells
- PMID: 34349610
- PMCID: PMC8328718
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5587297
Astaxanthin Inhibits Interleukin-6 Expression in Cerulein/Resistin-Stimulated Pancreatic Acinar Cells
Abstract
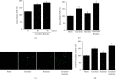
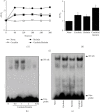
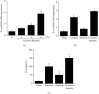
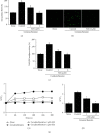
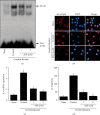
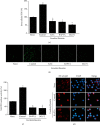
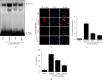
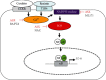
Acute pancreatitis is a common clinical condition with increasing the proinflammatory mediators, including interleukin-6 (IL-6). Obesity is a negative prognostic factor in acute pancreatitis. Obese patients with acute pancreatitis have a higher systemic inflammatory response rate. Levels of serum resistin, an adipocytokine secreted by fat tissues, increase with obesity. Cerulein, a cholecystokinin analog, induces calcium (Ca2+) overload, oxidative stress, and IL-6 expression in pancreatic acinar cells, which are hallmarks of acute pancreatitis. A recent study showed that resistin aggravates the expression of inflammatory cytokines in cerulein-stimulated pancreatic acinar cells. We aimed to investigate whether resistin amplifies cerulein-induced IL-6 expression and whether astaxanthin (ASX), an antioxidant carotenoid with anti-inflammatory properties, inhibits ceruelin/resistin-induced IL-6 expression in pancreatic acinar AR42J cells. We found that resistin enhanced intracellular Ca2+ levels, NADPH oxidase activity, intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, NF-κB activity, and IL-6 expression in cerulein-stimulated AR42J cells, which were inhibited by ASX in a dose-dependent manner. The calcium chelator BAPTA-AM inhibited cerulein/resistin-induced NADPH oxidase activation and ROS production. Antioxidant N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) and ML171, a specific NADPH oxidase 1 inhibitor, suppressed cerulein/resistin-induced ROS production, NF-κB activation, and IL-6 expression. In conclusion, ASX inhibits IL-6 expression, by reducing Ca2+ overload, NADPH oxidase-mediated ROS production, and NF-κB activity in cerulein/resistin-stimulated pancreatic acinar cells. Consumption of ASX-rich foods could be beneficial for preventing or delaying the incidence of obesity-associated acute pancreatitis.
Copyright © 2021 Min Seung Kwak et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
α‑lipoic acid inhibits cerulein/resistin‑induced expression of interleukin‑6 by activating peroxisome proliferator‑activated receptor‑γ in pancreatic acinar cells.Mol Med Rep. 2022 Aug;26(2):264. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12780. Epub 2022 Jun 22. Mol Med Rep. 2022. PMID: 35730599 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatitis-associated protein-1 suppresses apoptosis in cerulein-stimulated pancreatic acinar cells in response to nuclear factor-kappa B activation.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2019 Dec;70(6). doi: 10.26402/jpp.2019.6.04. Epub 2020 Feb 19. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 32084646
-
Docosahexaenoic acid inhibits IL-6 expression via PPARγ-mediated expression of catalase in cerulein-stimulated pancreatic acinar cells.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2017 Jul;88:60-68. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2017.05.011. Epub 2017 May 5. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28483666
-
Oxidative stress and inflammatory signaling in cerulein pancreatitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Dec 14;20(46):17324-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17324. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25516643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitory mechanism of lycopene on cytokine expression in experimental pancreatitis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011 Jul;1229:99-102. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06107.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011. PMID: 21793844 Review.
Cited by
-
The modulation of immune cell death in connection to microRNAs and natural products.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 20;15:1425602. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1425602. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39759512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
α‑lipoic acid inhibits cerulein/resistin‑induced expression of interleukin‑6 by activating peroxisome proliferator‑activated receptor‑γ in pancreatic acinar cells.Mol Med Rep. 2022 Aug;26(2):264. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12780. Epub 2022 Jun 22. Mol Med Rep. 2022. PMID: 35730599 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of adipokines for the severity of acute pancreatitis: a meta-analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Jan 13;24(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03126-w. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38218787 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of AMPK ameliorates acute severe pancreatitis by suppressing pancreatic acinar cell necroptosis in obese mice models.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Sep 30;9(1):363. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01655-z. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 37777514 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of current research on the modulation of NLRP3 inflammasome by traditional Chinese medicine to combat acute pancreatitis.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 Jul 16;12:1634132. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1634132. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40740190 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

