The Role of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Diabetic Cardiovascular Complications and Related Epigenetic Mechanisms
- PMID: 34349728
- PMCID: PMC8326758
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.598008
The Role of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Diabetic Cardiovascular Complications and Related Epigenetic Mechanisms
Abstract
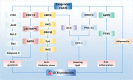
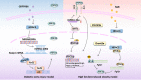
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), is an emerging metabolic regulator mediates multiple beneficial effects in the treatment of metabolic disorders and related complications. Recent studies showed that FGF21 acts as an important inhibitor in the onset and progression of cardiovascular complications of diabetes mellitus (DM). Furthermore, evidences discussed so far demonstrate that epigenetic modifications exert a crucial role in the initiation and development of DM-related cardiovascular complications. Thus, epigenetic modifications may involve in the function of FGF21 on DM-induced cardiovascular complications. Therefore, this review mainly interprets and delineates the recent advances of role of FGF21 in DM cardiovascular complications. Then, the possible changes of epigenetics related to the role of FGF21 on DM-induced cardiovascular complications are discussed. Thus, this article not only implies deeper understanding of the pathological mechanism of DM-related cardiovascular complications, but also provides the possible novel therapeutic strategy for DM-induced cardiovascular complications by targeting FGF21 and related epigenetic mechanism.
Keywords: FGF21; cardiovascular complications; diabetes; epigenetic; mechanisms.
Copyright © 2021 Xiao, Tang, Wang, Wang, Wang, Guo, Zhang and Gu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NRF2-Related Epigenetic Modifications in Cardiac and Vascular Complications of Diabetes Mellitus.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jun 25;12:598005. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.598005. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34248833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetics of methylation modifications in diabetic cardiomyopathy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 15;14:1119765. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1119765. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37008904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetics and diabetic cardiomyopathy.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011 Oct;94(1):14-21. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2011.05.033. Epub 2011 Jun 21. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011. PMID: 21696841 Review.
-
Epigenetic regulation in diabetic vascular complications.J Mol Endocrinol. 2019 Nov;63(4):R103-R115. doi: 10.1530/JME-19-0170. J Mol Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 31600719 Review.
-
Novel insights into DNA methylation and its critical implications in diabetic vascular complications.Biosci Rep. 2017 Mar 15;37(2):BSR20160611. doi: 10.1042/BSR20160611. Print 2017 Apr 30. Biosci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28183874 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
FGF21/FGFR1-β-KL cascade in cardiomyocytes modulates angiogenesis and inflammation under metabolic stress.Heliyon. 2023 Mar 30;9(4):e14952. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14952. eCollection 2023 Apr. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37123894 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Dietary Protein Intake Levels on Peripheral Circadian Rhythm in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 5;25(13):7373. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137373. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000480 Free PMC article.
-
Bo's abdominal acupuncture improves disordered metabolism in obese type 2 diabetic rats through regulating fibroblast growth factor 21 and its related adipokines.J Tradit Chin Med. 2023 Oct;43(6):1200-1208. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20231008.002. J Tradit Chin Med. 2023. PMID: 37946482 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Rendition of Adipose Genes Under Epigenetic Regulation: Revealing New Mechanisms of Obesity Occurrence.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Jul 11;47(7):540. doi: 10.3390/cimb47070540. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40729009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Circulating Biomarkers in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy.Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 23;12(9):2153. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12092153. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39335666 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

