Differentially Expressed Gene Pathways in the Conjunctiva of Sjögren Syndrome Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca
- PMID: 34349764
- PMCID: PMC8326832
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.702755
Differentially Expressed Gene Pathways in the Conjunctiva of Sjögren Syndrome Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca
Abstract
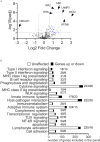
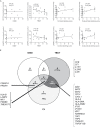
Sjögren syndrome (SS) is an autoimmune condition that targets the salivary and lacrimal glands, with cardinal clinical signs of dry eye (keratoconjunctivitis sicca, KCS) and dry mouth. The conjunctiva of SS patients is often infiltrated by immune cells that participate in the induction and maintenance of local inflammation. The purpose of this study was to investigate immune-related molecular pathways activated in the conjunctiva of SS patients. Female SS patients (n=7) and controls (n=19) completed a series of oral, ocular surface exams. Symptom severity scores were evaluated using validated questionnaires (OSDI and SANDE). All patients fulfilled the ACR/EULAR criteria for SS and the criteria for KCS. Fluorescein and lissamine green dye staining evaluated tear-break-up time (TBUT), corneal and conjunctival disease, respectively. Impression cytology of the temporal bulbar conjunctiva was performed to collect cells lysed and subjected to gene expression analysis using the NanoString Immunology Panel. 53/594 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were observed between SS and healthy controls; 49 DEGs were upregulated, and 4 were downregulated (TRAF5, TGFBI, KLRAP1, and CMKLRI). The top 10 DEGs in descending order were BST2, IFITM1, LAMP3, CXCL1, IL19, CFB, LY96, MX1, IL4R, CDKN1A. Twenty pathways had a global significance score greater or equal to 2. Spearman correlations showed that 29/49 upregulated DEGs correlated with either TBUT (inverse) or OSDI or conjunctival staining score (positive correlations). Venn diagrams identified that 26/29 DEGs correlated with TBUT, 5/26 DEGs correlated with OSDI, and 16/26 correlated with conjunctival staining scores. Five upregulated DEGs (CFB, CFI, IL1R1, IL2RG, IL4R) were uniquely negatively correlated with TBUT. These data indicate that the conjunctiva of SS patients exhibits a phenotype of immune activation, although some genes could be inhibitory. Some of the DEGs and pathways overlap with previous DEGs in salivary gland biopsies, but new DEGs were identified, and some of these correlated with symptoms and signs of dry eye. Our results indicate that gene analysis of conjunctiva imprints is a powerful tool to understand the pathogenesis of SS and develop new therapeutic targets.
Keywords: Sjögren syndrome; conjunctiva; dry eye; gene expression; immune pathways.
Copyright © 2021 de Paiva, Trujillo-Vargas, Schaefer, Yu, Britton and Pflugfelder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Correlation of clinical symptoms and signs with conjunctival gene expression in primary Sjögren syndrome dry eye patients.Ocul Surf. 2019 Jul;17(3):516-525. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2019.03.005. Epub 2019 Mar 21. Ocul Surf. 2019. PMID: 30905840
-
Differentially Expressed Tear Proteins in Sjögren's Syndrome Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2023 Jun 1;12(6):8. doi: 10.1167/tvst.12.6.8. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 37310735 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between habitual patient-reported symptoms and clinical signs among patients with dry eye of varying severity.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003 Nov;44(11):4753-61. doi: 10.1167/iovs.03-0270. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003. PMID: 14578396
-
Autoimmune Epithelitis and Chronic Inflammation in Sjögren's Syndrome-Related Dry Eye Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 30;22(21):11820. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111820. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mouse Models of Sjögren's Syndrome with Ocular Surface Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 30;21(23):9112. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239112. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33266081 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mouse Corneal Immune Cell Heterogeneity Revealed by Single-Cell RNA Sequencing.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024 Oct 1;65(12):29. doi: 10.1167/iovs.65.12.29. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024. PMID: 39432400 Free PMC article.
-
IFNα-IFITM1-ERK axis in corneal epithelial cell damage: implications for dry eye disease.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Jul 7;30(1):582. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02757-3. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40619436 Free PMC article.
-
A Distinguishable Peripheral Blood and Conjunctival Transcriptome and Gut Microbiome in Sjögren's Disease: A Pilot Study.Eye Contact Lens. 2025 May 2;51(7):304-311. doi: 10.1097/ICL.0000000000001186. Eye Contact Lens. 2025. PMID: 40314468 Free PMC article.
-
Sjögren's Versus Non-Sjögren's Ocular Features: Similar Symptoms, But Significantly Worse Signs.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024 Jan 2;65(1):23. doi: 10.1167/iovs.65.1.23. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024. PMID: 38193760 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the Potential Link Between Dermatomyositis and Cancer.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Dec 3;17:10163-10182. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S480744. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39649426 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakamura T, Nishida K, Dota A, Matsuki M, Yamanishi K, Kinoshita S. Elevated Expression of Transglutaminase 1 and Keratinization-Related Proteins in Conjunctiva in Severe Ocular Surface Disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci (2001) 42:549–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

