Development and Validation of a Convolutional Neural Network for Automated Detection of Scaphoid Fractures on Conventional Radiographs
- PMID: 34350413
- PMCID: PMC8329964
- DOI: 10.1148/ryai.2021200260
Development and Validation of a Convolutional Neural Network for Automated Detection of Scaphoid Fractures on Conventional Radiographs
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the performance of a convolutional neural network (CNN) to that of 11 radiologists in detecting scaphoid bone fractures on conventional radiographs of the hand, wrist, and scaphoid.
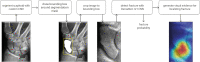
Materials and methods: At two hospitals (hospitals A and B), three datasets consisting of conventional hand, wrist, and scaphoid radiographs were retrospectively retrieved: a dataset of 1039 radiographs (775 patients [mean age, 48 years ± 23 {standard deviation}; 505 female patients], period: 2017-2019, hospitals A and B) for developing a scaphoid segmentation CNN, a dataset of 3000 radiographs (1846 patients [mean age, 42 years ± 22; 937 female patients], period: 2003-2019, hospital B) for developing a scaphoid fracture detection CNN, and a dataset of 190 radiographs (190 patients [mean age, 43 years ± 20; 77 female patients], period: 2011-2020, hospital A) for testing the complete fracture detection system. Both CNNs were applied consecutively: The segmentation CNN localized the scaphoid and then passed the relevant region to the detection CNN for fracture detection. In an observer study, the performance of the system was compared with that of 11 radiologists. Evaluation metrics included the Dice similarity coefficient (DSC), Hausdorff distance (HD), sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC).
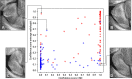
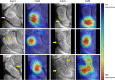
Results: The segmentation CNN achieved a DSC of 97.4% ± 1.4 with an HD of 1.31 mm ± 1.03. The detection CNN had sensitivity of 78% (95% CI: 70, 86), specificity of 84% (95% CI: 77, 92), PPV of 83% (95% CI: 77, 90), and AUC of 0.87 (95% CI: 0.81, 0.91). There was no difference between the AUC of the CNN and that of the radiologists (0.87 [95% CI: 0.81, 0.91] vs 0.83 [radiologist range: 0.79-0.85]; P = .09).
Conclusion: The developed CNN achieved radiologist-level performance in detecting scaphoid bone fractures on conventional radiographs of the hand, wrist, and scaphoid.Keywords: Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), Deep Learning Algorithms, Machine Learning Algorithms, Feature Detection-Vision-Application Domain, Computer-Aided DiagnosisSee also the commentary by Li and Torriani in this issue.Supplemental material is available for this article.©RSNA, 2021.
Keywords: Computer-Aided Diagnosis; Convolutional Neural Network (CNN); Deep Learning Algorithms; Feature Detection-Vision-Application Domain; Machine Learning Algorithms.
2021 by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures of Conflicts of Interest: N.H. disclosed no relevant relationships. E.S. disclosed no relevant relationships. B.V. disclosed no relevant relationships. S. Bruijnen disclosed no relevant relationships. B.M. disclosed no relevant relationships. M.d.J. disclosed no relevant relationships. S.D. disclosed no relevant relationships. S. Bollen disclosed no relevant relationships. S.S. disclosed no relevant relationships. M.d.R. Activities related to the present article: employed by Radboudumc. Activities not related to the present article: disclosed no relevant relationships. Other relationships: disclosed no relevant relationships. A.S. Activities related to the present article: disclosed no relevant relationships. Activities not related to the present article: author is consultant for Aidence (detection and volumetric assessment of lung nodules on CT using deep learning). Other relationships: disclosed no relevant relationships. W.H. disclosed no relevant relationships. T.S. disclosed no relevant relationships. L.L.S.O. disclosed no relevant relationships. E.P. disclosed no relevant relationships. B.v.G. Activities related to the present article: disclosed no relevant relationships. Activities not related to the present article: grants from Thirona, Delft Imaging Systems, MeVis Medical Solutions; royalties from Thirona, Delft Imaging Systems, MeVis Medical Solutions; stock/stock options from Thirona. Other relationships: disclosed no relevant relationships. M.R. disclosed no relevant relationships.
Figures

References
-
- de Zwart AD, Beeres FJP, Rhemrev SJ, Bartlema K, Schipper IB. Comparison of MRI, CT and bone scintigraphy for suspected scaphoid fractures. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2016;42(6):725–731. - PubMed
-
- Tiel-van Buul MM, van Beek EJ, Broekhuizen AH, Bakker AJ, Bos KE, van Royen EA. Radiography and scintigraphy of suspected scaphoid fracture. A long-term study in 160 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1993;75(1):61–65. - PubMed
-
- Gibney B, Smith M, Moughty A, Kavanagh EC, Hynes D, MacMahon PJ. Incorporating cone-beam CT into the diagnostic algorithm for suspected radiocarpal fractures: A new standard of care?. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2019;213(5):1117–1123. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

