Subgroup analysis of the AFTER I-O study: a retrospective study on the efficacy and safety of subsequent molecular targeted therapy after immune-oncology therapy in Japanese patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 34350454
- PMCID: PMC8558912
- DOI: 10.1093/jjco/hyab114
Subgroup analysis of the AFTER I-O study: a retrospective study on the efficacy and safety of subsequent molecular targeted therapy after immune-oncology therapy in Japanese patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Subgroup analysis of the AFTER I-O study: a retrospective study on the efficacy and safety of subsequent molecular targeted therapy after immune-oncology therapy in Japanese patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2021 Dec 1;51(12):1770. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyab161. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34585728 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: We performed subgroup analyses of the AFTER I-O study to clarify the association of time-to-treatment failure (TTF) and discontinuation reason of prior immune-oncology (I-O) therapy, and molecular targeted therapy (TT) regimen with the outcomes of TT after I-O.
Methods: The data of Japanese metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients treated with TT after nivolumab (NIVO) (CheckMate 025) or NIVO + ipilimumab (IPI) (CheckMate 214) were retrospectively analyzed. The objective response rates (ORRs), progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) of TT after I-O were analyzed by subgroups: TTF (<6 or ≥6 months) and discontinuation reason of prior I-O (progression or adverse events), and TT regimen (sunitinib or axitinib). We also analyzed PFS2 of prior I-O and OS from first-line therapy.
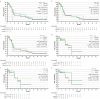
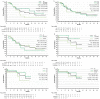
Results: The ORR and median PFS of TT after NIVO and NIVO+IPI among the subgroups was 17-36% and 20-44%, and 7.1-11.6 months and 16.3-not reached (NR), respectively. The median OS of TT after NIVO was longer in patients with longer TTF of NIVO and treated with axitinib. Conversely, median OS of TT after NIVO+IPI was similar among subgroups. The median PFS2 of NIVO and NIVO+IPI was 36.7 and 32.0 months, respectively. The median OS from first-line therapy was 70.5 months for patients treated with NIVO and NR with NIVO+IPI. The safety profile of each TT after each I-O was similar to previous reports.
Conclusions: The efficacy of TT after NIVO or NIVO+IPI was favorable regardless of the TTF and discontinuation reason of prior I-O, and TT regimen.
Keywords: ipilimumab; molecular targeted therapy; nivolumab; renal cell carcinoma.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures


References
-
- Naito S, Yamamoto N, Takayama T, et al. . Prognosis of Japanese metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients in the cytokine era: a cooperative group report of 1463 patients. Eur Urol 2010;57:317–26. - PubMed
-
- Harada K, Nozawa M, Uemura M, et al. . Treatment patterns and outcomes in patients with unresectable or metastatic renal cell carcinoma in Japan. Int J Urol 2019;26:202–10. - PubMed
-
- Albiges L, Fay AP, Xie W, et al. . Efficacy of targeted therapies after PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer 2015;51:2580–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

