Unbiased automated quantitation of ROS signals in live retinal neurons of Drosophila using Fiji/ImageJ
- PMID: 34350780
- PMCID: PMC10288391
- DOI: 10.2144/btn-2021-0006
Unbiased automated quantitation of ROS signals in live retinal neurons of Drosophila using Fiji/ImageJ
Abstract
Numerous imaging modules are utilized to study changes that occur during cellular processes. Besides qualitative (immunohistochemical) or semiquantitative (Western blot) approaches, direct quantitation method(s) for detecting and analyzing signal intensities for disease(s) biomarkers are lacking. Thus, there is a need to develop method(s) to quantitate specific signals and eliminate noise during live tissue imaging. An increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) such as superoxide (O2•-) radicals results in oxidative damage of biomolecules, which leads to oxidative stress. This can be detected by dihydroethidium staining in live tissue(s), which does not rely on fixation and helps prevent stress on tissues. However, the signal-to-noise ratio is reduced in live tissue staining. We employ the Drosophila eye model of Alzheimer's disease as a proof of concept to quantitate ROS in live tissue by adapting an unbiased method. The method presented here has a potential application for other live tissue fluorescent images.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Drosophila; ImageJ; automated quantitation; confocal microscopy; dihydroethidium; live cell imaging; neurodegeneration; oxidative stress; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Figures
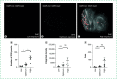

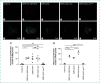
References
-
- Sies H, Jones DP. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signalling agents. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 21(7), 363–383 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
