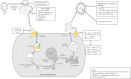
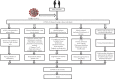
Obesity, a major risk factor for immunity and severe outcomes of COVID-19
- PMID: 34350941
- PMCID: PMC8380923
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20210979
Obesity, a major risk factor for immunity and severe outcomes of COVID-19
Abstract
An influenza-like virus named severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) is responsible for COVID-19 disease and spread worldwide within a short time. COVID-19 has now become a significant concern for public health. Obesity is highly prevalent worldwide and is considered a risk factor for impairing the adaptive immune system. Although diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease (CVD), and renal failure are considered the risk factors for COVID-19, obesity is not yet well-considered. The present study approaches establishing a systemic association between the prevalence of obesity and its impact on immunity concerning the severe outcomes of COVID-19 utilizing existing knowledge. Overall study outcomes documented the worldwide prevalence of obesity, its effects on immunity, and a possible underlying mechanism covering obesity-related risk pathways for the severe outcomes of COVID-19. Overall understanding from the present study is that being an immune system impairing factor, the role of obesity in the severe outcomes of COVID-19 is worthy.
Keywords: ACE-2; COVID-19; Immunity; Morbidity; Obesity; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Worldometer: COVID Live Update:. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/?utm_campaign=homeAdvegas1?
-
- Fuk-Woo Chan J., Yuan S., Kok K.-H., Kai-Wang To K., Chu H., Yang J.et al. . (2020) Articles A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: a study of a family cluster. Lancet 395, 514–523 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30154-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous