Single-cell transcriptome profiling of the human developing spinal cord reveals a conserved genetic programme with human-specific features
- PMID: 34351410
- PMCID: PMC8353162
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.199711
Single-cell transcriptome profiling of the human developing spinal cord reveals a conserved genetic programme with human-specific features
Abstract
The spinal cord receives input from peripheral sensory neurons and controls motor output by regulating muscle innervating motor neurons. These functions are carried out by neural circuits comprising molecularly distinct neuronal subtypes generated in a characteristic spatiotemporal arrangement from progenitors in the embryonic neural tube. To gain insight into the diversity and complexity of cells in the developing human neural tube, we used single-cell mRNA sequencing to profile cervical and thoracic regions in four human embryos of Carnegie stages (CS) CS12, CS14, CS17 and CS19 from gestational weeks 4-7. Analysis of progenitor and neuronal populations from the neural tube and dorsal root ganglia identified dozens of distinct cell types and facilitated the reconstruction of the differentiation pathways of specific neuronal subtypes. Comparison with mouse revealed overall similarity of mammalian neural tube development while highlighting some human-specific features. These data provide a catalogue of gene expression and cell type identity in the human neural tube that will support future studies of sensory and motor control systems. The data can be explored at https://shiny.crick.ac.uk/scviewer/neuraltube/.
Keywords: Developmental patterning; Human; Neuronal subtype identity; Single-cell transcriptome; Spinal cord.
© 2021. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures


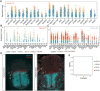



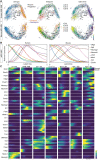

References
-
- Chiu, I. M., Barrett, L. B., Williams, E. K., Strochlic, D. E., Lee, S., Weyer, A. D., Lou, S., Bryman, G. S., Roberson, D. P., Ghasemlou, N.et al. (2014). Transcriptional profiling at whole population and single cell levels reveals somatosensory neuron molecular diversity. eLife 3, e04660. 10.7554/eLife.04660.034 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

