Population Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Burosumab in Adult and Pediatric Patients With X-linked Hypophosphatemia
- PMID: 34352114
- PMCID: PMC9292737
- DOI: 10.1002/jcph.1950
Population Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Burosumab in Adult and Pediatric Patients With X-linked Hypophosphatemia
Abstract
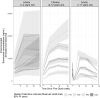
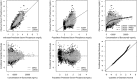
Burosumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody against fibroblast growth factor 23, which has been approved to treat X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH) in adult and pediatric patients. The present work describes the pharmacokinetics (PK) of burosumab and the pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) relationship between burosumab and serum phosphorus in adult and pediatric patients with XLH. A total of 2844 measurable serum concentrations of burosumab and 6047 measurable serum concentrations of phosphorus in 277 subjects from 9 clinical studies were included in the population PK and PK-PD modeling. The serum concentration of burosumab following a subcutaneous administration was well described by a population PK model comprising a first-order absorption, 1-compartmental distribution, and a linear elimination. The relationship between serum burosumab and serum phosphorus was adequately described by a sigmoid maximal efficacy model. Body weight was the only covariate associated with PK and PK-PD parameters. No other intrinsic factors affected PK or PK-PD relationship in adult and pediatric patients with XLH. Further simulations helped to guide the dosing regimen of burosumab in adult and pediatric patients with XLH including age groups with no clinical data.
Keywords: X-linked hypophosphatemia; burosumab; pharmacodynamics; pharmacokinetics; serum phosphorus.
© 2021 The Authors. The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American College of Clinical Pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
S.L., J.T., and K.M. are current employees of Ultragenyx. J.S. and M.S.R. are former Ultragenyx employees and were employed at Ultragenyx Pharmaceuticals Inc. when these studies were conducted. N.H.G. is an employee of Certara and does not have any conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pharmacodynamic Exposure-Response Analysis of Fracture Count Data Following Treatment with Burosumab in Patients with XLH.J Clin Pharmacol. 2025 Feb;65(2):253-260. doi: 10.1002/jcph.6140. Epub 2024 Sep 30. J Clin Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39344278 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained Efficacy and Safety of Burosumab, a Monoclonal Antibody to FGF23, in Children With X-Linked Hypophosphatemia.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Feb 17;107(3):813-824. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgab729. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022. PMID: 34636899 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Burosumab Therapy in Children with X-Linked Hypophosphatemia.N Engl J Med. 2018 May 24;378(21):1987-1998. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1714641. N Engl J Med. 2018. PMID: 29791829 Clinical Trial.
-
Burosumab for Pediatric X-Linked Hypophosphatemia.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2021 Jun;19(3):271-277. doi: 10.1007/s11914-021-00669-9. Epub 2021 May 10. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2021. PMID: 33970403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of burosumab compared with conventional therapy in patients with X-linked hypophosphatemia: A systematic review.Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2024 May 17;68:e230242. doi: 10.20945/2359-4292-2023-0242. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2024. PMID: 38788147 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pharmacodynamic Exposure-Response Analysis of Fracture Count Data Following Treatment with Burosumab in Patients with XLH.J Clin Pharmacol. 2025 Feb;65(2):253-260. doi: 10.1002/jcph.6140. Epub 2024 Sep 30. J Clin Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39344278 Free PMC article.
-
Nivolumab and ipilimumab population pharmacokinetics in support of pediatric dose recommendations-Going beyond the body-size effect.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2024 Mar;13(3):476-493. doi: 10.1002/psp4.13098. Epub 2024 Jan 8. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38115545 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical practice recommendations for the diagnosis and management of X-linked hypophosphataemia.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2025 May;21(5):330-354. doi: 10.1038/s41581-024-00926-x. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39814982 Review.
-
Osteomalacia in Adults: A Practical Insight for Clinicians.J Clin Med. 2023 Apr 5;12(7):2714. doi: 10.3390/jcm12072714. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37048797 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Holm I, Econs M, Carpenter T. Familial hypophosphatemia and related disorders. In: FH G, H J, eds. Pediatric Bone: Biology & Diseases. 2nd ed. San Diego, CA: Elsevier; 2012:699‐726.
-
- Burnett CH, Dent CE, Harper C, Warland BJ. Vitamin D‐resistant rickets Analysis of twenty‐four pedigrees with hereditary and sporadic cases. Am J Medicine. 1964;36(2):222‐232. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter TO. New perspectives on the biology and treatment of X‐linked hypophosphatemic rickets. Pediatr Clin N Am. 1997;44(2):443‐466. - PubMed
-
- Yamazaki Y, Tamada T, Kasai N, et al. Anti‐FGF23 neutralizing antibodies show the physiological role and structural features of FGF23. J Bone Miner Res. 2008;23(9):1509‐1518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

