A multi-center retrospective cohort study defines the spectrum of kidney pathology in Coronavirus 2019 Disease (COVID-19)
- PMID: 34352311
- PMCID: PMC8328528
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2021.07.015
A multi-center retrospective cohort study defines the spectrum of kidney pathology in Coronavirus 2019 Disease (COVID-19)
Abstract
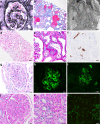
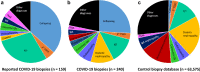
Kidney failure is common in patients with Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19), resulting in increased morbidity and mortality. In an international collaboration, 284 kidney biopsies were evaluated to improve understanding of kidney disease in COVID-19. Diagnoses were compared to five years of 63,575 native biopsies prior to the pandemic and 13,955 allograft biopsies to identify diseases that have increased in patients with COVID-19. Genotyping for APOL1 G1 and G2 alleles was performed in 107 African American and Hispanic patients. Immunohistochemistry for SARS-CoV-2 was utilized to assess direct viral infection in 273 cases along with clinical information at the time of biopsy. The leading indication for native biopsy was acute kidney injury (45.4%), followed by proteinuria with or without concurrent acute kidney injury (42.6%). There were more African American patients (44.6%) than patients of other ethnicities. The most common diagnosis in native biopsies was collapsing glomerulopathy (25.8%), which was associated with high-risk APOL1 genotypes in 91.7% of cases. Compared to the five-year biopsy database, the frequency of myoglobin cast nephropathy and proliferative glomerulonephritis with monoclonal IgG deposits was also increased in patients with COVID-19 (3.3% and 1.7%, respectively), while there was a reduced frequency of chronic conditions (including diabetes mellitus, IgA nephropathy, and arterionephrosclerosis) as the primary diagnosis. In transplants, the leading indication was acute kidney injury (86.4%), for which rejection was the predominant diagnosis (61.4%). Direct SARS-CoV-2 viral infection was not identified. Thus, our multi-center large case series identified kidney diseases that disproportionately affect patients with COVID-19 and demonstrated a high frequency of APOL1 high-risk genotypes within this group, with no evidence of direct viral infection within the kidney.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; acute kidney injury; coronavirus; kidney biopsy; renal pathology.
Copyright © 2021 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

