Gray matter blood-brain barrier water exchange dynamics are reduced in progressive multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 34355458
- PMCID: PMC9291753
- DOI: 10.1111/jon.12912
Gray matter blood-brain barrier water exchange dynamics are reduced in progressive multiple sclerosis
Abstract
Background and purpose: To compare transcapillary wall water exchange, a putative marker of cerebral metabolic health, in brain T2 white matter (WM) lesions and normal appearing white and gray matter (NAWM and NAGM, respectively) in individuals with progressive multiple sclerosis (PMS) and healthy controls (HC).
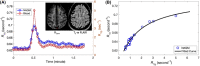
Methods: Dynamic-contrast-enhanced 7T MRI data were obtained from 19 HC and 23 PMS participants. High-resolution pharmacokinetic parametric maps representing tissue microvascular and microstructural properties were created by shutter-speed (SS) paradigm modeling to obtain estimates of blood volume fraction (vb ), water molecule capillary efflux rate constant (kpo ), and the water capillary wall permeability surface area product (Pw S ≡ vb *kpo ). Linear regression models were used to investigate differences in (i) kpo and Pw S between groups in NAWM and NAGM, and (ii) between WM lesions and NAWM in PMS.
Results: High-resolution parametric maps were produced to visualize tissue classes and resolve individual WM lesions. Normal-appearing gray matter kpo and Pw S were significantly decreased in PMS compared to HC (p ≤ .01). Twenty-one T2 WM lesions were analyzed in 10 participants with PMS. kpo was significantly decreased in WM lesions compared to PMS NAWM (p < .0001).
Conclusions: Transcapillary water exchange is reduced in PMS NAGM compared to HC and is further reduced in PMS WM lesions, suggesting pathologically impaired brain metabolism. kpo provides a sensitive measure of cerebral metabolic activity and/or coupling, and can be mapped at higher spatial resolution than conventional imaging techniques assessing metabolic activity.
Keywords: DCE-MRI; blood-brain barrier; cerebral metabolism; neurodegeneration; progressive multiple sclerosis.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Neuroimaging published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society of Neuroimaging.
Figures

References
-
- Lassmann H, van Horssen J, Mahad D. Progressive multiple sclerosis: pathology and pathogenesis. Nat Rev Neurol 2012;8:647‐56. - PubMed
-
- Hauser SL, Chan JR, Oksenberg JR. Multiple sclerosis: prospects and promise. Ann Neurol 2013;74:317‐27. - PubMed
-
- Lassmann H. The pathologic substrate of magnetic resonance alterations in multiple sclerosis. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 2008;18:563‐76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

