The potential of ex vivo lung perfusion on improving organ quality and ameliorating ischemia reperfusion injury
- PMID: 34355495
- PMCID: PMC8925042
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.16784
The potential of ex vivo lung perfusion on improving organ quality and ameliorating ischemia reperfusion injury
Abstract
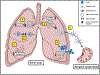
Allogeneic lung transplantation (LuTx) is considered the treatment of choice for a broad range of advanced, progressive lung diseases resistant to conventional treatment regimens. Ischemia reperfusion injury (IRI) occurring upon reperfusion of the explanted, ischemic lung during implantation remains a crucial mediator of primary graft dysfunction (PGD) and early allo-immune responses. Ex vivo lung perfusion (EVLP) displays an advanced technique aiming at improving lung procurement and preservation. Indeed, previous clinical trials have demonstrated a reduced incidence of PGD following LuTx utilizing EVLP, while long-term outcomes are yet to be evaluated. Mechanistically, EVLP may alleviate donor lung inflammation through reconditioning the injured lung and diminishing IRI through storing the explanted lung in a non-ischemic, perfused, and ventilated status. In this work, we review potential mechanisms of EVLP that may attenuate IRI and improve organ quality. Moreover, we dissect experimental treatment approaches during EVLP that may further attenuate inflammatory events deriving from tissue ischemia, shear forces or allograft rejection associated with LuTx.
Keywords: ex vivo lung perfusion; graft function; ischemia reperfusion injury; lung transplantation.
© 2021 The Authors. American Journal of Transplantation published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Chambers DC, Cherikh WS, Harhay MO, Hayes D Jr., Hsich E, Khush KK et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-sixth adult lung and heart-lung transplantation Report-2019; Focus theme: Donor and recipient size match. J Heart Lung Transplant 2019;38(10):1042–1055. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Copeland H, Hayanga JWA, Neyrinck A, MacDonald P, Dellgren G, Bertolotti A et al. Donor heart and lung procurement: A consensus statement. J Heart Lung Transplant 2020;39(6):501–517. - PubMed
-
- den Hengst WA, Gielis JF, Lin JY, Van Schil PE, De Windt LJ, Moens AL. Lung ischemia-reperfusion injury: a molecular and clinical view on a complex pathophysiological process. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2010;299(5):H1283–1299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

