Evaluation of Auto-Planning for Left-Side Breast Cancer After Breast-Conserving Surgery Based on Geometrical Relationship
- PMID: 34355592
- PMCID: PMC8358503
- DOI: 10.1177/15330338211033050
Evaluation of Auto-Planning for Left-Side Breast Cancer After Breast-Conserving Surgery Based on Geometrical Relationship
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate (1) the performance of the Auto-Planning module embedded in the Pinnacle treatment planning system (TPS) with 30 left-side breast cancer plans and (2) the dose-distance correlations between dose-based patients and overlap volume histogram-based (OVH) patients.
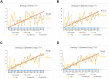
Method: A total of 30 patients with left-side breast cancer after breast-conserving surgery were enrolled in this study. The clinical manual-planning (MP) and the Auto-Planning (AP) plans were generated by Monaco and by the Auto-Planning module in Pinnacle respectively. The geometric information between organ at risk (OAR) and planning target volume (PTV) of each patient was described by the OVH. The AP and MP plans were ranked to compare with the geometry-based patients from OVH. The Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient (R) was used to describe the correlations between dose-based patients (APs and MPs) and geometry-based patients (OVH). Dosimetric differences between MP and AP plans were evaluated with statistical analysis.
Result: The correlation coefficient (mean R = 0.71) indicated that the AP plans have a high correlation with geometry-based patients from OVH, whereas the correlation coefficient (mean R = 0.48) shows a weak correlation between MP plans and geometry-based patients. The dosimetric comparison revealed a statistically significant improvement in the ipsilateral lung V5Gy and V10Gy, and in the heart V5Gy of AP plans compared to MP plans, while statistical reduction was seen in PTV V107% for MP plans compared to AP plans.
Conclusion: The overall results of AP plans were superior to MP plans. The dose distribution in AP plans was more consistent with the distance-dose relationship described by OVH. After eliminating the interference of human factors, the AP was able to provide more stable and objective plans for radiotherapy patients.
Keywords: OVH; VMAT; auto-planning; breast cancer; geometrical relationship.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A.Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG); Darby S, McGale P, Correa C, et al. Effect of radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery on 10-year recurrence and 15-year breast cancer death: meta-analysis of individual patient data for 10,801 women in 17 randomised trials. Lancet. 2011;378(9804):1707–1716. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mansouri S, Naim A, Glaria L, Marsiglia H. Dosimetric evaluation of 3-D conformal and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for breast cancer after conservative surgery. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(11):4727–4732. - PubMed
-
- Fong A, Bromley R, Beat M, Vien D, Dineley J, Morgan G. Dosimetric comparison of intensity modulated radiotherapy techniques and standard wedged tangents for whole breast radiotherapy. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2009;53(1):92–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

