The Importance of Being PI3K in the RAS Signaling Network
- PMID: 34356110
- PMCID: PMC8303222
- DOI: 10.3390/genes12071094
The Importance of Being PI3K in the RAS Signaling Network
Abstract
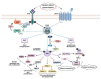
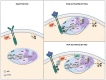
Ras proteins are essential mediators of a multitude of cellular processes, and its deregulation is frequently associated with cancer appearance, progression, and metastasis. Ras-driven cancers are usually aggressive and difficult to treat. Although the recent Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of the first Ras G12C inhibitor is an important milestone, only a small percentage of patients will benefit from it. A better understanding of the context in which Ras operates in different tumor types and the outcomes mediated by each effector pathway may help to identify additional strategies and targets to treat Ras-driven tumors. Evidence emerging in recent years suggests that both oncogenic Ras signaling in tumor cells and non-oncogenic Ras signaling in stromal cells play an essential role in cancer. PI3K is one of the main Ras effectors, regulating important cellular processes such as cell viability or resistance to therapy or angiogenesis upon oncogenic Ras activation. In this review, we will summarize recent advances in the understanding of Ras-dependent activation of PI3K both in physiological conditions and cancer, with a focus on how this signaling pathway contributes to the formation of a tumor stroma that promotes tumor cell proliferation, migration, and spread.
Keywords: PI3-Kinase; Ras oncogenes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

