Influences of Lavender Essential Oil Inhalation on Stress Responses during Short-Duration Sleep Cycles: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 34356287
- PMCID: PMC8303840
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare9070909
Influences of Lavender Essential Oil Inhalation on Stress Responses during Short-Duration Sleep Cycles: A Pilot Study
Abstract
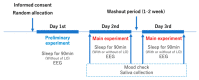
Lavender essential oil (LEO) was reported to improve sleep quality. We investigated the influence of aromatherapy by testing the effects of LEO on stress responses during a short-duration sleep in a single-blind, randomized, crossover trial. The subjects were twelve healthy adults who were nonsmokers without any known disease and who were not prescribed medications, and nine of these completed the study. After the subjects had fallen asleep, they were sprayed with LEO using an aroma diffuser. Before and after 90 min of sleep, α-amylase, chromogranin A (CgA), and cortisol levels in saliva were measured as objective stress indicators, and the Japanese version of the UWIST Mood Adjective Checklist was used as a subjective indicator. A comparison of changes before and after sleep, with and without LEO, revealed that the cortisol level did not significantly change; however, α-amylase (p < 0.05) and CgA (p < 0.01) levels significantly decreased after LEO inhalation. A mood test indicated no change in mood before and after sleep, with or without LEO. Since α-amylase and CgA reflect the sympathetic nervous system response, these results indicate that LEO aromatherapy during a short-duration sleep cycle suppresses the stress response, especially that of the sympathetic nervous system.
Keywords: antistress effect; aromatherapy; chromogranin A; cortisol; lavender essential oil; α-amylase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Alanko K. Handbook of Occupational Dermatology. Springer; New York, NK, USA: 2000. Aromatherapists; pp. 811–813.
-
- Donatello N.N., Emer A.A., Salm D.C., Ludtke D.D., Bordignon S.A.S.R., Ferreira J.K., Salgado A.S.I., Venzke D., Bretanha L.C., Micke G.A. Lavandula angustifolia essential oil inhalation reduces mechanical hyperalgesia in a model of inflammatory and neuropathic pain: The involvement of opioid and cannabinoid receptors. J. Neuroimmunol. 2020;340:577145. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2020.577145. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

