Genetic Investigation of Inverse Psoriasis
- PMID: 34357026
- PMCID: PMC8306123
- DOI: 10.3390/life11070654
Genetic Investigation of Inverse Psoriasis
Abstract
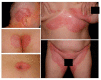
Inverse psoriasis is considered to be a rare variant of plaque-type psoriasis and is associated with significantly impaired quality of life. Clinical manifestations and treatment options are somewhat different for each subtype. Identifying genetic variants that contribute to the susceptibility of different types of psoriasis might improve understanding of the etiology of the disease. Since we have no current knowledge about the genetic background of inverse psoriasis, whole exome sequencing was used to comprehensively assess genetic variations in five patients with exclusively inverse lesions. We detected six potentially pathogenic rare (MAF < 0.01) sequence variants that occurred in all investigated patients. The corresponding mutated genes were FN1, FBLN1, MYH7B, MST1R, RHOD, and SCN10A. Several mutations identified in this study are known to cause disease, but roles in psoriasis or other papulosquamous diseases have not previously been reported. Interestingly, potentially causative variants of established psoriasis-susceptibility genes were not identified. These outcomes are in agreement with our hypothesis that the inverse subtype is a different entity from plaque-type psoriasis.
Keywords: WES; genetic background; inverse psoriasis; pathogenic gene variants; whole exome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, the writing of the manuscript, or the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Wang G., Li C., Gao T., Liu Y. Clinical analysis of 48 cases of inverse psoriasis: A hospital-based study. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2005;15:176–178. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous